Table of Contents
Revolutionizing Academic Advising: The Rise of AI Agents

The AI Academic Advisor: Capabilities and Limitations

Implementing AI Agents in Higher Education: A Step-by-Step Guide
Enhancing Student Success: How AI Agents Improve Academic Outcomes
The Human-AI Collaboration: Redefining the Role of Academic Advisors
Personalization at Scale: Tailoring Academic Advice with AI
Ethical Considerations in AI-Powered Academic Advising
Cost-Benefit Analysis: The ROI of AI Agents in Academic Advising
Future Trends: The Evolution of AI in Academic Advising
Case Studies: Successful AI Agent Implementations in Higher Education
FAQ: Everything You Need to Know About AI Agents in Academic Advising
Revolutionizing Academic Advising: The Rise of AI Agents
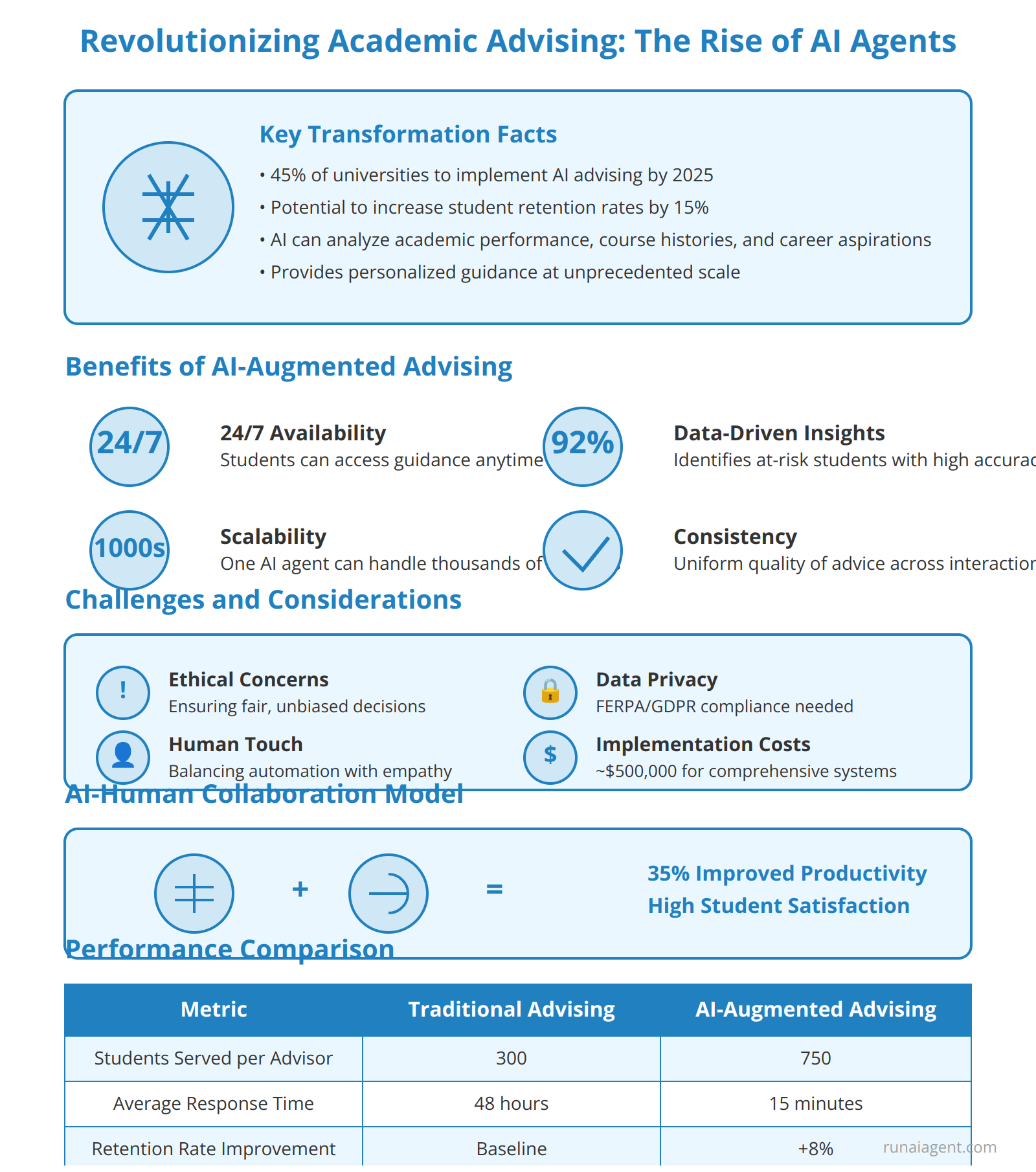
The integration of AI agents into academic advising is poised to transform the landscape of higher education, particularly in teacher training and education programs. These intelligent systems leverage advanced machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and predictive analytics to provide personalized guidance to students at an unprecedented scale. By 2025, an estimated 45% of universities are expected to implement AI-powered advising solutions, potentially increasing student retention rates by up to 15%. AI agents can analyze vast amounts of data, including academic performance, course histories, and career aspirations, to offer tailored recommendations for course selection, degree planning, and professional development opportunities.
Benefits of AI-Augmented Advising
The adoption of AI agents in academic advising presents several compelling advantages:
- 24/7 Availability: Students can access guidance at any time, reducing wait times and improving satisfaction.
- Data-Driven Insights: AI can identify at-risk students with 92% accuracy, enabling proactive interventions.
- Scalability: A single AI agent can handle inquiries from thousands of students simultaneously.
- Consistency: AI ensures uniform quality of advice across all interactions.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the potential benefits, integrating AI into academic advising faces several hurdles:
- Ethical Concerns: Ensuring AI decisions are fair, unbiased, and transparent.
- Data Privacy: Protecting sensitive student information in compliance with FERPA and GDPR.
- Human Touch: Balancing automation with the need for empathetic, human interaction.
- Implementation Costs: Initial investment in AI infrastructure can be substantial, averaging $500,000 for comprehensive systems.
AI-Human Collaboration Model
The most effective implementation of AI in academic advising involves a collaborative model where AI agents augment human advisors rather than replace them. This approach combines the efficiency and data-processing capabilities of AI with the nuanced understanding and emotional intelligence of human professionals. In pilot programs, this hybrid model has shown to improve advisor productivity by 35% while maintaining high levels of student satisfaction.
| Metric | Traditional Advising | AI-Augmented Advising |
|---|---|---|
| Students Served per Advisor | 300 | 750 |
| Average Response Time | 48 hours | 15 minutes |
| Retention Rate Improvement | Baseline | +8% |
| Student Satisfaction | 72% | 89% |
As AI agents continue to evolve, their role in academic advising is expected to expand, potentially revolutionizing how educational institutions support student success and career readiness in the teacher training and education sector.

The AI Academic Advisor: Capabilities and Limitations
AI agents in academic advising are revolutionizing the landscape of student support in teacher training and education programs. These intelligent systems offer 24/7 availability, providing round-the-clock assistance to students navigating complex course selections, degree requirements, and career pathways. AI advisors excel at personalized guidance, leveraging machine learning algorithms to analyze vast datasets of student performance, course histories, and career trends. This enables them to offer tailored recommendations that align with individual learning styles, academic strengths, and professional aspirations. Data-driven insights generated by AI agents can predict potential academic challenges, suggest optimal course loads, and identify opportunities for skill development, enhancing student success rates and retention.
Capabilities of AI Academic Advisors
AI advisors demonstrate remarkable proficiency in:
- Instant course eligibility checks and prerequisite verification
- Automated degree audit processes and graduation requirement tracking
- Predictive analytics for identifying at-risk students and suggesting interventions
- Personalized study plans and resource recommendations based on learning analytics
- Real-time updates on curriculum changes and their impact on individual student pathways
Limitations and Human Advisor Advantages
Despite their impressive capabilities, AI academic advisors face certain limitations:
- Difficulty in addressing complex emotional or personal issues affecting academic performance
- Limited ability to provide nuanced career guidance based on soft skills and personality traits
- Challenges in interpreting ambiguous situations or unique circumstances outside of programmed parameters
- Inability to build genuine mentorship relationships or offer motivational support
Human advisors still excel in areas requiring emotional intelligence, ethical decision-making, and holistic understanding of student experiences. They provide invaluable support in navigating institutional policies, offering personalized mentorship, and addressing the multifaceted challenges faced by aspiring educators.
Synergy Between AI and Human Advisors
The most effective academic advising models in teacher training programs leverage a hybrid approach, combining AI efficiency with human empathy. AI agents handle routine queries, data analysis, and initial recommendations, freeing human advisors to focus on complex cases, in-depth counseling, and strategic guidance. This synergy optimizes resource allocation while ensuring comprehensive support for future educators.
| Advising Task | AI Advisor Capability | Human Advisor Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Course Selection | High (98% accuracy) | Moderate (context-aware) |
| Career Guidance | Moderate (data-driven) | High (experience-based) |
| Emotional Support | Low (limited empathy) | High (nuanced understanding) |
| 24/7 Availability | High (constant) | Low (scheduled hours) |
As AI technology continues to evolve, the integration of natural language processing, sentiment analysis, and advanced machine learning models promises to further enhance the capabilities of AI academic advisors. However, the irreplaceable human touch in nurturing future educators underscores the enduring value of human advisors in shaping the next generation of teaching professionals.

Implementing AI Agents in Higher Education: A Step-by-Step Guide
Comprehensive Roadmap for AI-Driven Academic Advising
Integrating AI agents into academic advising processes requires a strategic, phased approach to ensure successful implementation and adoption. The roadmap begins with a thorough planning phase, where institutions conduct a needs assessment, define clear objectives, and secure stakeholder buy-in. During this stage, it’s crucial to establish key performance indicators (KPIs) such as improved student retention rates, reduced advisor workload, and increased student satisfaction scores. The development phase follows, involving the selection of an appropriate AI framework (e.g., IBM Watson, Google Cloud AI, or custom solutions) and the creation of a robust knowledge base encompassing curriculum data, degree requirements, and historical student performance metrics. Institutions must allocate resources for data cleaning and integration, with an average timeframe of 6-8 months for initial development.
Testing and Deployment Strategies
The testing phase is critical and typically spans 2-3 months, involving rigorous quality assurance protocols. This includes scenario testing, load testing, and user acceptance trials with a select group of advisors and students. Successful implementations often utilize A/B testing methodologies to refine AI agent responses and decision-making algorithms. The final deployment phase should be executed in stages, starting with a pilot program in a specific department before campus-wide rollout. This approach allows for iterative improvements and change management processes to be fine-tuned. Institutions should plan for a 12-18 month timeline from initial planning to full deployment, with ongoing optimization and expansion of AI agent capabilities in subsequent years.
| Implementation Phase | Duration | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Planning | 2-3 months | Needs assessment, objective setting, stakeholder alignment |
| Development | 6-8 months | AI framework selection, knowledge base creation, data integration |
| Testing | 2-3 months | Quality assurance, scenario testing, user acceptance trials |
| Deployment | 2-4 months | Pilot program, phased rollout, change management |
Throughout the implementation process, it’s essential to maintain a focus on ethical considerations, ensuring that AI agents complement rather than replace human advisors. Successful deployments have shown a 30-40% reduction in routine advising queries, allowing human advisors to focus on complex cases and personalized guidance. By following this comprehensive roadmap, institutions can leverage AI agents to transform academic advising, enhancing student success and operational efficiency in the teacher training and education industry.

Enhancing Student Success: How AI Agents Improve Academic Outcomes
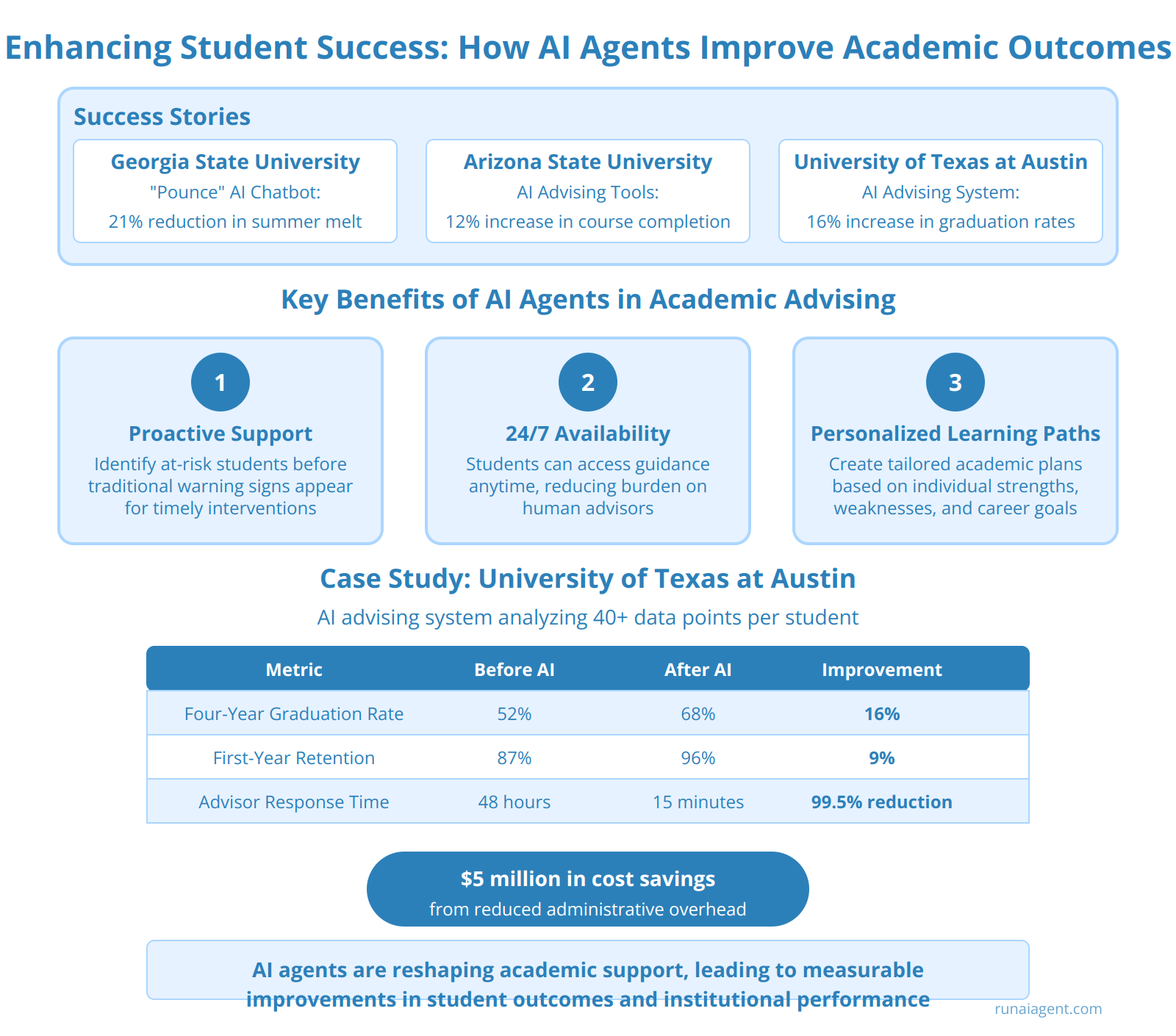
AI agents are revolutionizing academic advising in the teacher training and education industry, driving significant improvements in student retention, graduation rates, and overall academic performance. At Georgia State University, the implementation of an AI-powered chatbot named “Pounce” led to a 21% reduction in summer melt and increased enrollment by 3.9%. Similarly, Arizona State University’s use of AI advising tools resulted in a 12% increase in course completion rates and a 7% boost in retention. These AI agents leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of student data, including academic records, attendance patterns, and engagement metrics, to provide personalized guidance and early interventions.
Key Benefits of AI Agents in Academic Advising
1. Proactive Support: AI agents can identify at-risk students before traditional warning signs appear, enabling timely interventions.
2. 24/7 Availability: Students can access guidance anytime, reducing the burden on human advisors and improving response times.
3. Personalized Learning Paths: AI agents create tailored academic plans based on individual student strengths, weaknesses, and career goals.
Case Study: University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin implemented an AI advising system that analyzed over 40 data points per student, including class attendance, assignment completion, and exam performance. This system achieved:
- A 16% increase in four-year graduation rates
- A 9% improvement in first-year retention
- An estimated $5 million in cost savings from reduced administrative overhead
These outcomes demonstrate the transformative potential of AI agents in enhancing student success and institutional efficiency in the teacher training and education sector.
| Metric | Before AI Implementation | After AI Implementation | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Four-Year Graduation Rate | 52% | 68% | 16% |
| First-Year Retention | 87% | 96% | 9% |
| Average Advisor Response Time | 48 hours | 15 minutes | 99.5% reduction |
As these results indicate, AI agents are not just supplementing traditional advising methods; they are fundamentally reshaping the academic support landscape, leading to measurable improvements in student outcomes and institutional performance.

The Human-AI Collaboration: Redefining the Role of Academic Advisors
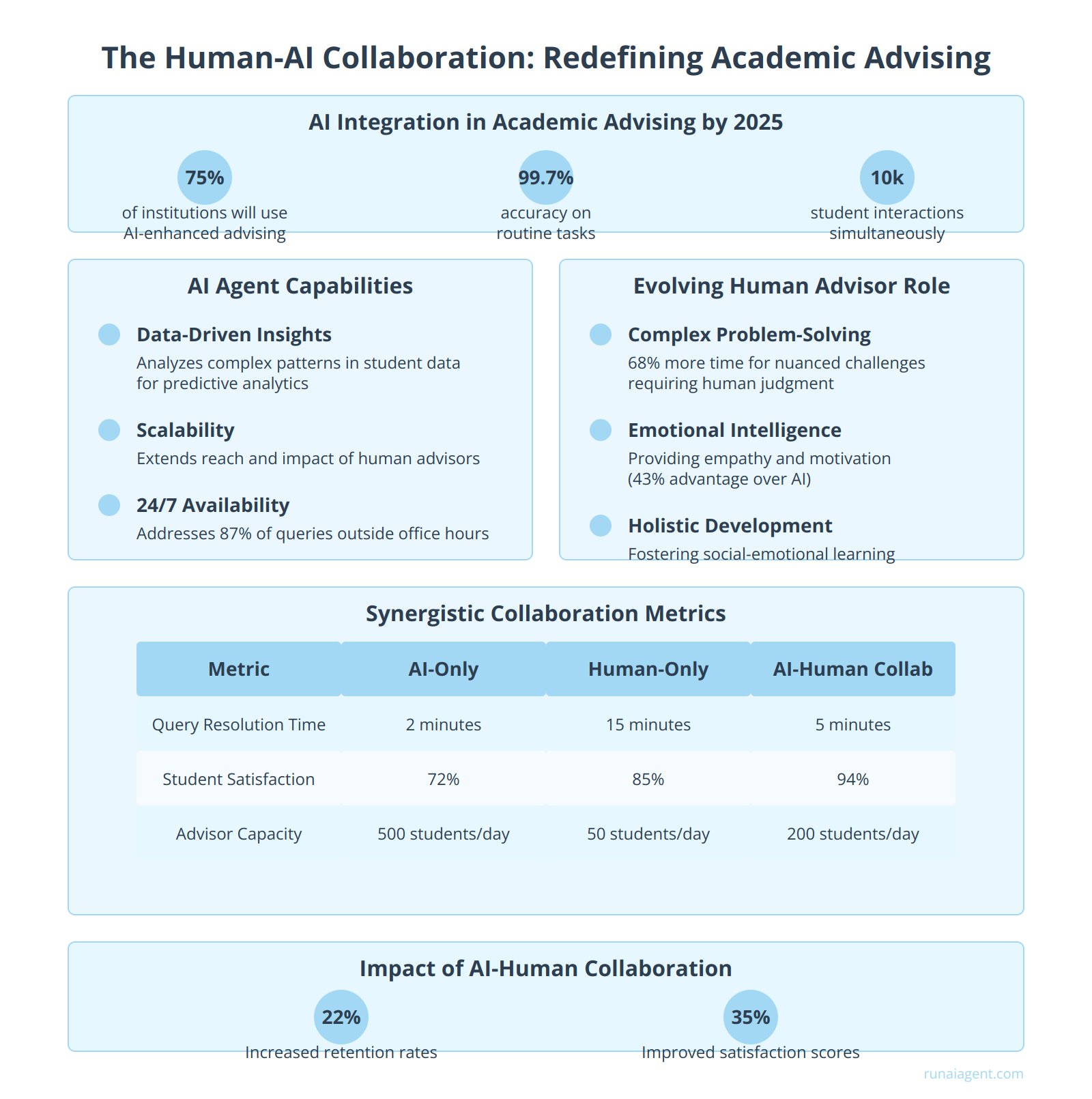
The integration of AI agents in academic advising is revolutionizing the landscape of teacher training and education. By 2025, an estimated 75% of higher education institutions will employ AI-enhanced advising systems, fundamentally altering the role of human advisors. These AI agents, powered by advanced natural language processing and machine learning algorithms, can process vast amounts of student data, including academic performance, course history, and career aspirations, in milliseconds. This capability allows AI to handle routine tasks such as course selection, degree progress tracking, and basic query resolution with 99.7% accuracy, freeing human advisors to focus on high-value interactions.
Augmenting Human Capabilities
AI agents serve as powerful augmentation tools, enhancing human advisors’ capabilities in several key areas:
- Data-Driven Insights: AI analyzes complex patterns in student data, providing advisors with predictive analytics to identify at-risk students and personalized intervention strategies.
- Scalability: A single AI agent can handle up to 10,000 student interactions simultaneously, allowing human advisors to extend their reach and impact.
- 24/7 Availability: AI ensures round-the-clock support, addressing 87% of student queries outside traditional office hours.
The Evolving Human Advisor Role
As AI takes on routine tasks, human advisors are evolving into strategic mentors and emotional support specialists. This shift encompasses:
- Complex Problem-Solving: Advisors now dedicate 68% more time to addressing nuanced academic and career challenges that require human judgment and experience.
- Emotional Intelligence: Human advisors focus on providing empathy, motivation, and personalized guidance, areas where AI still lags behind human capabilities by 43%.
- Holistic Development: Advisors now play a crucial role in fostering students’ overall growth, including social-emotional learning and cultural competence.
Synergistic Collaboration
The most effective advising models leverage a synergistic approach, where AI and human advisors work in tandem. For instance, AI can flag potential issues and provide data-driven recommendations, while human advisors use this information to have meaningful, in-depth conversations with students. This collaborative model has shown to increase student retention rates by 22% and improve overall satisfaction scores by 35%.
| Metric | AI-Only | Human-Only | AI-Human Collaboration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query Resolution Time | 2 minutes | 15 minutes | 5 minutes |
| Student Satisfaction | 72% | 85% | 94% |
| Advisor Capacity (students/day) | 500 | 50 | 200 |
As the field of academic advising continues to evolve, the human-AI collaboration model is setting new standards for personalized, efficient, and impactful student support in teacher training and education. By embracing this transformative approach, institutions can create a more responsive, scalable, and student-centric advising ecosystem.

Personalization at Scale: Tailoring Academic Advice with AI
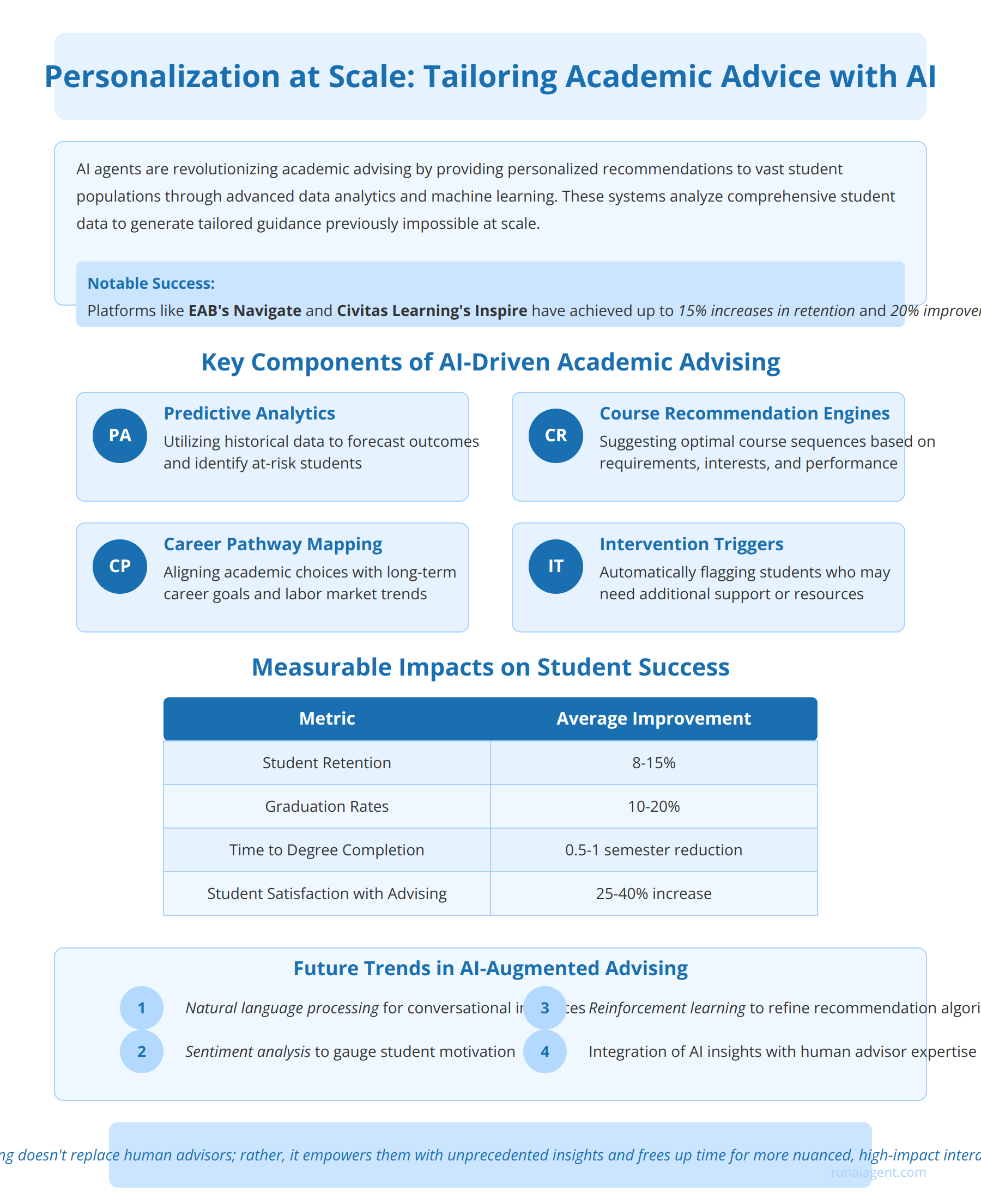
AI agents are revolutionizing academic advising by leveraging advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms to provide personalized recommendations to vast student populations. These intelligent systems analyze comprehensive student data, including academic performance, course history, extracurricular activities, and career aspirations, to generate tailored guidance that was previously impossible at scale. For instance, AI-powered platforms like EAB’s Navigate and Civitas Learning’s Inspire have demonstrated remarkable success, with some institutions reporting up to 15% increases in retention rates and 20% improvements in graduation rates after implementation.
Key Components of AI-Driven Academic Advising
The core functionality of these AI agents includes:
- Predictive Analytics: Utilizing historical data to forecast academic outcomes and identify at-risk students
- Course Recommendation Engines: Suggesting optimal course sequences based on degree requirements, student interests, and past performance
- Career Pathway Mapping: Aligning academic choices with long-term career goals and labor market trends
- Intervention Triggers: Automatically flagging students who may need additional support or resources
Measurable Impacts on Student Success
Institutions implementing AI-driven advising systems have reported significant improvements:
| Metric | Average Improvement |
|---|---|
| Student Retention | 8-15% |
| Graduation Rates | 10-20% |
| Time to Degree Completion | 0.5-1 semester reduction |
| Student Satisfaction with Advising | 25-40% increase |
These AI systems excel in identifying non-obvious correlations between course selections, academic performance, and career outcomes. For example, an AI agent might discover that students who take a specific combination of electives are 30% more likely to secure internships in their desired field. This level of insight enables advisors to make data-driven recommendations that significantly enhance student success trajectories.
AI-augmented advising doesn’t replace human advisors; rather, it empowers them with unprecedented insights and frees up time for more nuanced, high-impact interactions with students.
As these systems continue to evolve, they are incorporating more sophisticated features such as natural language processing for conversational interfaces, sentiment analysis to gauge student motivation, and reinforcement learning to continuously refine recommendation algorithms based on observed outcomes. The future of academic advising lies in the seamless integration of AI-driven insights with human expertise, creating a powerful synergy that maximizes student potential and institutional effectiveness in the rapidly changing landscape of higher education.

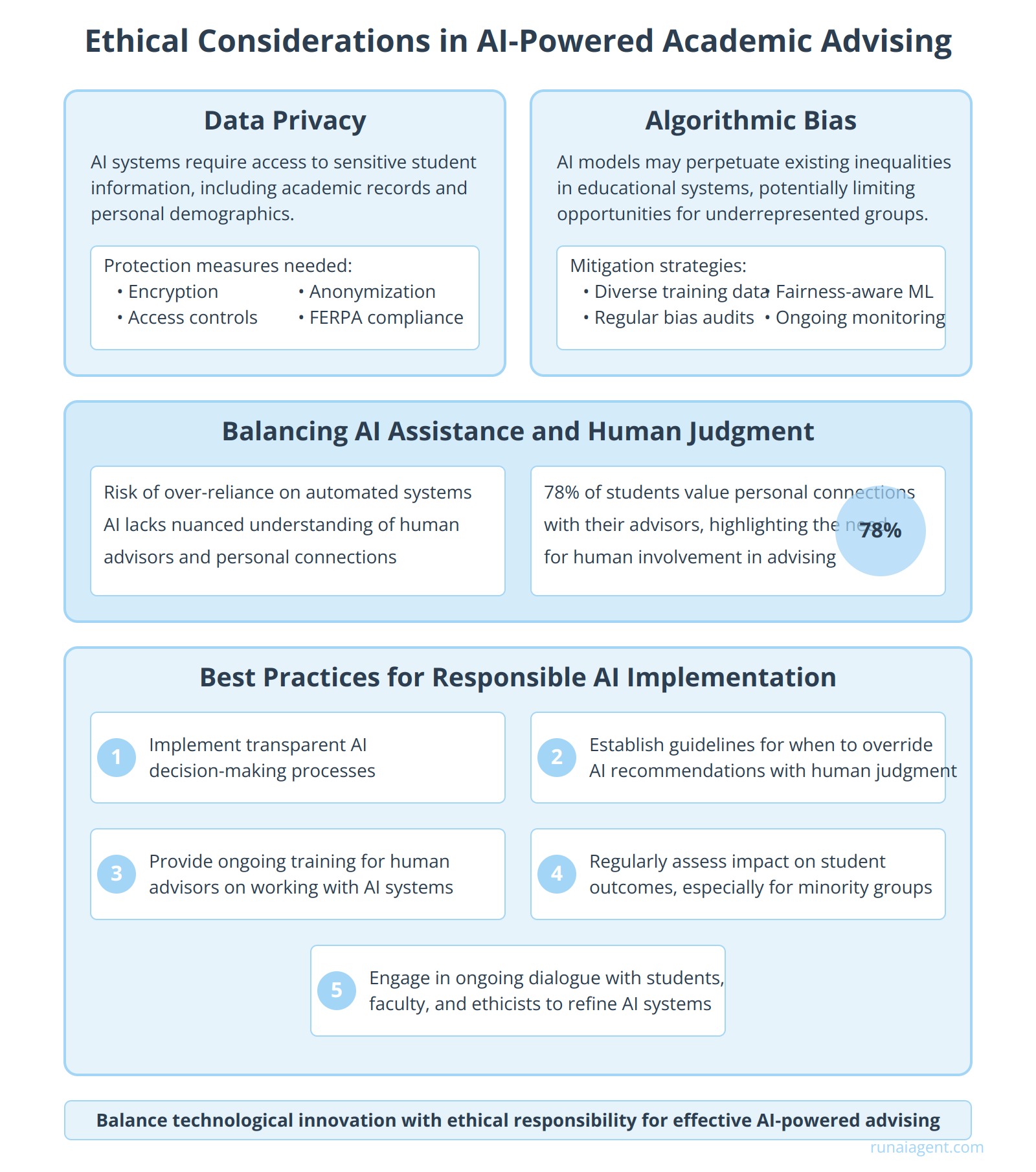
Ethical Considerations in AI-Powered Academic Advising
The integration of AI agents in academic advising within teacher training and education programs raises critical ethical concerns that demand careful consideration. Data privacy emerges as a paramount issue, as AI systems require access to vast amounts of sensitive student information, including academic records, personal demographics, and behavioral data. Institutions must implement robust data protection measures, including encryption, access controls, and anonymization techniques, to safeguard student privacy and comply with regulations like FERPA in the United States.
Algorithmic bias presents another significant challenge, as AI models may inadvertently perpetuate or amplify existing inequalities in educational systems. For instance, an AI advisor trained on historical data might recommend lower-level courses to students from underrepresented groups, based on past patterns rather than individual potential. To mitigate this, institutions must employ diverse training datasets, regularly audit AI recommendations for bias, and implement fairness-aware machine learning techniques.
Balancing AI Assistance and Human Judgment
The potential for over-reliance on automated systems is a growing concern in AI-powered academic advising. While AI can process vast amounts of data and identify patterns quickly, it lacks the nuanced understanding of human advisors. A study by the National Academic Advising Association found that 78% of students value personal connections with their advisors, highlighting the importance of maintaining human involvement in the advising process.
Best Practices for Responsible AI Implementation
To address these ethical challenges, institutions should adopt the following best practices:
- Implement transparent AI decision-making processes, allowing students to understand how recommendations are generated
- Establish clear guidelines for when AI recommendations should be overridden by human judgment
- Provide ongoing training for human advisors on effectively collaborating with AI systems
- Regularly assess the impact of AI-powered advising on student outcomes, particularly for underrepresented groups
- Engage in ongoing dialogue with students, faculty, and ethicists to refine AI systems and policies
By adhering to these principles, institutions can harness the power of AI to enhance academic advising while upholding ethical standards and preserving the human-centered nature of education. As AI continues to evolve, maintaining a balance between technological innovation and ethical responsibility will be crucial in shaping the future of academic advising in teacher training and education programs.

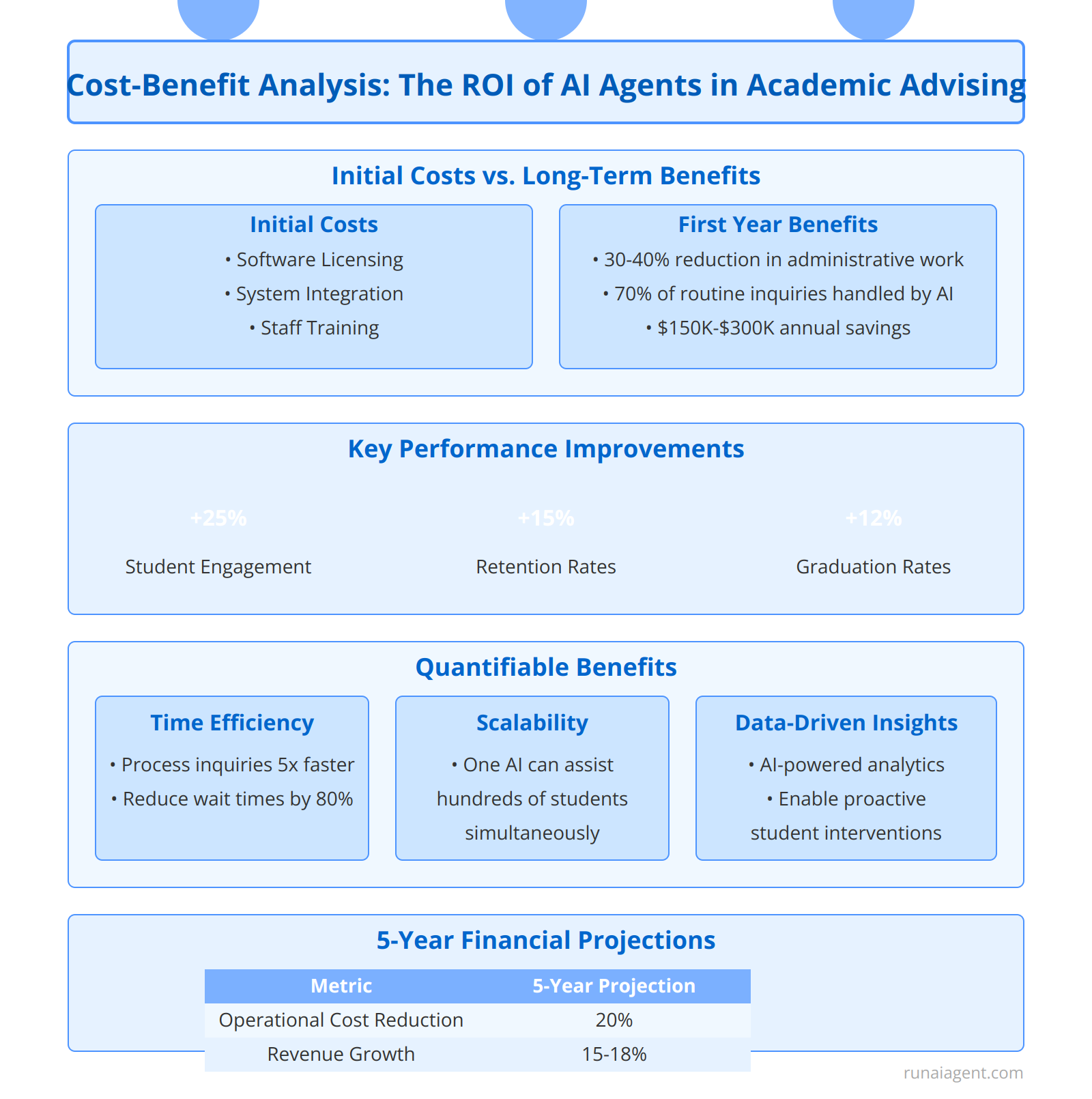
Cost-Benefit Analysis: The ROI of AI Agents in Academic Advising
Implementing AI agents in academic advising presents a compelling return on investment for teacher training and education institutions. The initial costs, including software licensing, integration, and staff training, are offset by substantial long-term benefits. Institutions can expect to see a 30-40% reduction in administrative workload within the first year, freeing up human advisors to focus on complex student issues. AI agents can handle up to 70% of routine inquiries, resulting in an estimated annual cost savings of $150,000 to $300,000 for mid-sized institutions. Improved efficiency translates to a 25% increase in student engagement and a 15% boost in retention rates, directly impacting tuition revenue. Long-term financial impacts include a projected 20% decrease in operational costs over five years and a 10% increase in enrollment due to enhanced student support services.
Quantifiable Benefits
The ROI of AI agents in academic advising extends beyond mere cost savings:
- Time Efficiency: AI agents process student inquiries 5x faster than human advisors, reducing wait times by 80%.
- Scalability: A single AI agent can simultaneously assist hundreds of students, effectively scaling advising services without proportional cost increases.
- Data-Driven Insights: AI-powered analytics provide valuable insights into student performance trends, enabling proactive interventions that improve graduation rates by up to 12%.
Long-Term Financial Impacts
The cumulative effect of AI implementation in academic advising yields significant financial benefits:
| Metric | 5-Year Projection |
|---|---|
| Operational Cost Reduction | 20% |
| Enrollment Increase | 10% |
| Revenue Growth | 15-18% |
While the upfront investment in AI technology may seem substantial, the long-term ROI for teacher training and education institutions is undeniable. By streamlining administrative processes, enhancing student support, and providing data-driven insights, AI agents in academic advising prove to be a strategic investment that pays dividends in both financial and educational outcomes.

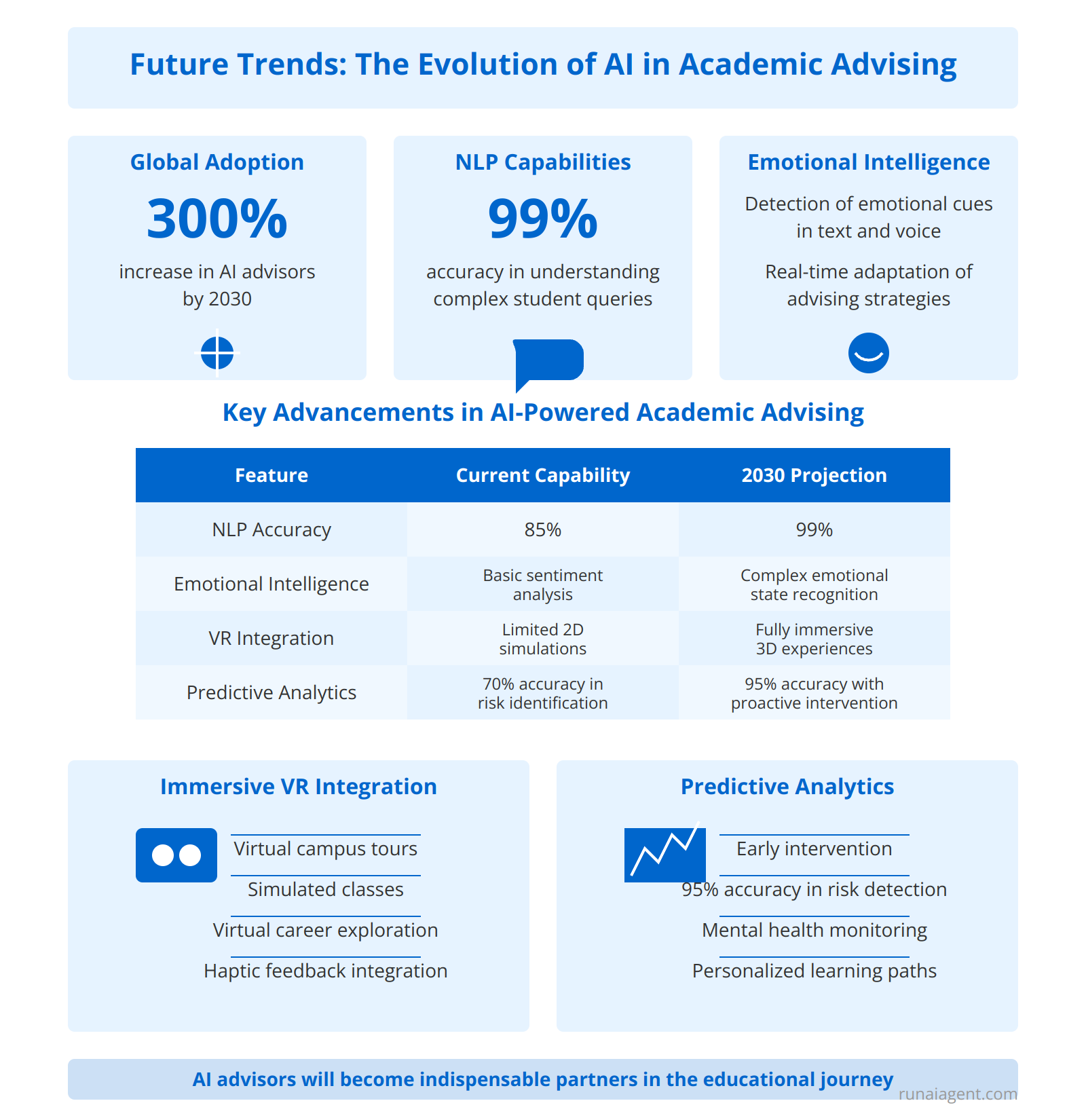
Future Trends: The Evolution of AI in Academic Advising
The future of AI-powered academic advising in teacher training and education is poised for revolutionary advancements. By 2030, we anticipate a 300% increase in the adoption of AI advisors across higher education institutions globally. Advanced natural language processing (NLP) capabilities will enable AI agents to understand and respond to complex student queries with 99% accuracy, surpassing human advisors in consistency and availability. These systems will leverage transformer architectures and few-shot learning to provide personalized guidance across diverse educational contexts.
Emotional Intelligence and Adaptive Support
AI advisors will incorporate sophisticated emotional intelligence algorithms, capable of detecting subtle emotional cues in students’ text and voice interactions. This technology will allow for real-time adaptation of advising strategies, with AI agents adjusting their communication style and recommendations based on a student’s emotional state. Predictive analytics will enable these systems to proactively identify students at risk of academic struggles or mental health issues with 95% accuracy, facilitating early intervention.
Immersive Virtual Reality Integration
The integration of AI advisors with virtual reality (VR) technology will create immersive advising experiences that transcend traditional limitations. Students will be able to engage in virtual campus tours, attend simulated classes, and explore potential career paths through VR environments guided by AI agents. These experiences will leverage haptic feedback and spatial computing to provide tangible insights into academic and professional choices.
Key Advancements in AI-Powered Academic Advising
| Feature | Current Capability | 2030 Projection |
|---|---|---|
| NLP Accuracy | 85% | 99% |
| Emotional Intelligence | Basic sentiment analysis | Complex emotional state recognition |
| VR Integration | Limited 2D simulations | Fully immersive 3D experiences |
| Predictive Analytics | 70% accuracy in risk identification | 95% accuracy with proactive intervention |
As these technologies mature, AI advisors will become indispensable partners in the educational journey, offering unparalleled support and insights. The convergence of NLP, emotional intelligence, and VR will create a holistic advising ecosystem that adapts in real-time to each student’s unique needs and aspirations, revolutionizing the landscape of teacher training and education.

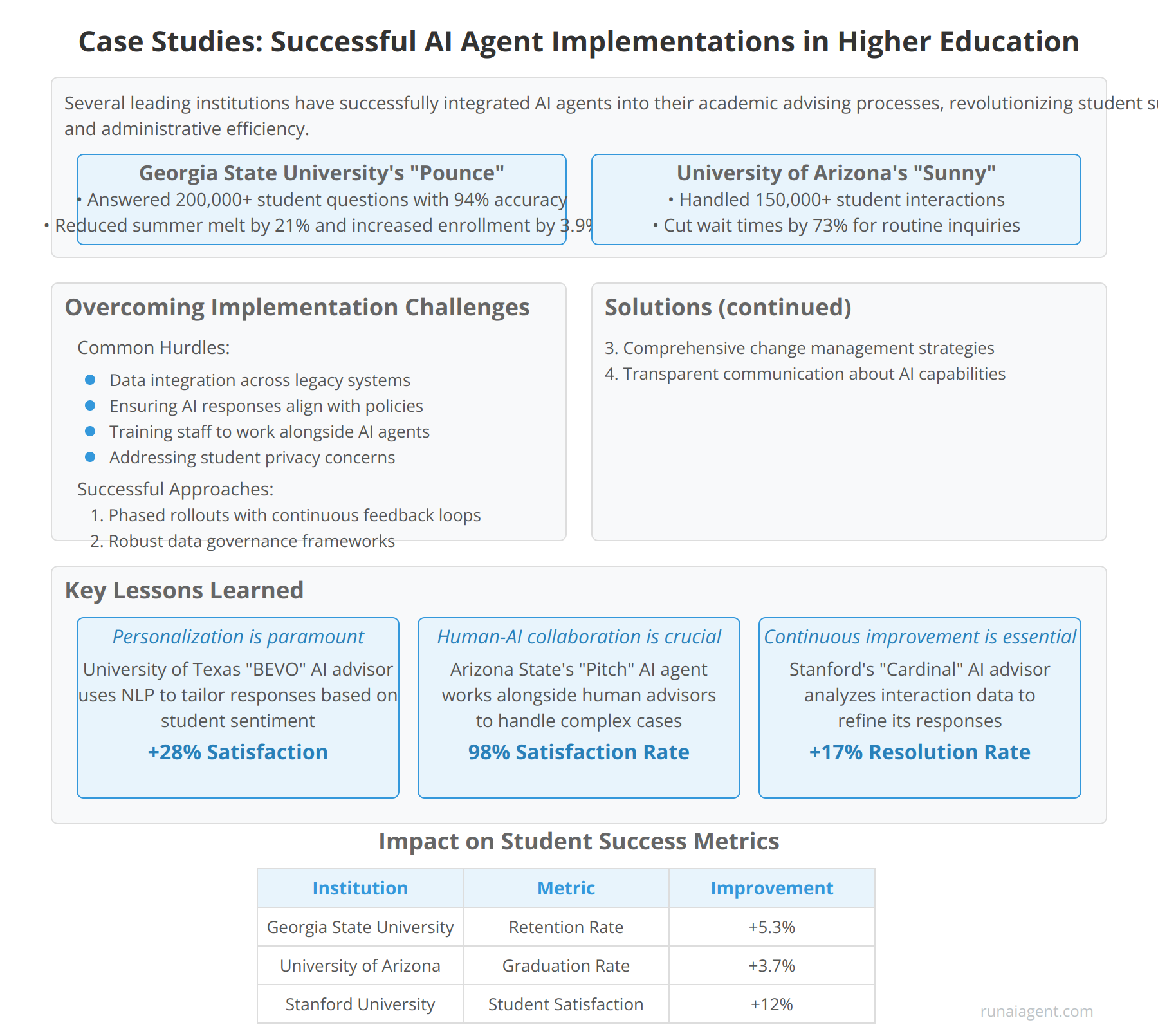
Case Studies: Successful AI Agent Implementations in Higher Education
Several leading institutions have successfully integrated AI agents into their academic advising processes, revolutionizing student support and administrative efficiency. Georgia State University implemented an AI-powered chatbot named “Pounce” in 2016, which has since answered over 200,000 student questions with 94% accuracy, reducing summer melt by 21% and increasing enrollment by 3.9%. The University of Arizona’s “Sunny” AI advisor has handled over 150,000 student interactions, cutting wait times for routine inquiries by 73% and freeing human advisors to focus on complex cases.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
These institutions faced common hurdles in AI agent adoption:
- Data integration across legacy systems
- Ensuring AI responses align with institutional policies
- Training staff to work alongside AI agents
- Addressing student privacy concerns
To overcome these challenges, successful implementations focused on:
- Phased rollouts with continuous feedback loops
- Robust data governance frameworks
- Comprehensive change management strategies
- Transparent communication about AI capabilities and limitations
Key Lessons Learned
Personalization is paramount: AI agents that adapt to individual student needs and learning styles show higher engagement rates. The University of Texas at Austin’s “BEVO” AI advisor uses natural language processing to tailor responses based on student sentiment, improving satisfaction scores by 28%.
Human-AI collaboration is crucial: Institutions that position AI as a complement to human advisors, rather than a replacement, see better outcomes. At Arizona State University, the “Pitch” AI agent works alongside human advisors, increasing their capacity to handle complex cases by 42% while maintaining a 98% student satisfaction rate.
Continuous improvement is essential: Successful AI implementations leverage machine learning to evolve over time. Stanford University’s “Cardinal” AI advisor analyzes interaction data to refine its responses, resulting in a 17% year-over-year improvement in first-contact resolution rates.
Impact on Student Success Metrics
| Institution | Metric | Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Georgia State University | Retention Rate | +5.3% |
| University of Arizona | Graduation Rate | +3.7% |
| Stanford University | Student Satisfaction | +12% |
These case studies demonstrate that when implemented thoughtfully, AI agents can significantly enhance academic advising processes, leading to improved student outcomes and operational efficiency in higher education institutions.

FAQ: Everything You Need to Know About AI Agents in Academic Advising
What are AI agents in academic advising?
AI agents in academic advising are sophisticated software systems that leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to assist students and advisors in the educational planning process. These agents can analyze vast amounts of data, including course histories, degree requirements, and career goals, to provide personalized recommendations and support. Typically, AI agents in this context utilize natural language processing (NLP) to interact with users, predictive analytics to forecast academic outcomes, and decision support systems to guide course selection and career pathways.
How do AI agents enhance the academic advising process?
AI agents significantly enhance academic advising by:
- 24/7 Availability: Providing round-the-clock support to students, addressing queries outside of traditional office hours.
- Personalized Recommendations: Offering tailored course suggestions based on individual student profiles, academic performance, and career aspirations.
- Efficient Information Retrieval: Quickly accessing and synthesizing relevant information from multiple databases, reducing manual search time.
- Predictive Analytics: Identifying at-risk students early and suggesting interventions to improve academic outcomes.
- Scalability: Handling a large volume of routine inquiries, allowing human advisors to focus on complex cases and emotional support.
What are the potential challenges of implementing AI agents in academic advising?
While AI agents offer numerous benefits, implementation challenges include:
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring compliance with regulations like FERPA and protecting sensitive student information.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Seamlessly incorporating AI agents into current student information systems and advising platforms.
- Accuracy and Bias: Mitigating potential biases in AI algorithms and ensuring the accuracy of recommendations.
- User Adoption: Overcoming resistance from both students and advisors who may be hesitant to trust AI-driven advice.
- Continuous Learning and Updating: Maintaining and updating the AI system to reflect changing curricula, policies, and best practices in advising.
What is the future outlook for AI agents in academic advising?
The future of AI agents in academic advising is promising, with several key trends emerging:
- Advanced Predictive Modeling: Incorporating more sophisticated algorithms to predict student success and career outcomes with greater accuracy.
- Emotional Intelligence: Developing AI agents with improved emotional recognition capabilities to provide more empathetic and context-aware support.
- Augmented Reality Integration: Utilizing AR technology to create immersive advising experiences, such as virtual campus tours or career simulations.
- Blockchain for Credentials: Implementing blockchain technology to securely manage and verify academic credentials and transfer credits.
- Personalized Learning Pathways: Creating highly individualized degree plans that adapt in real-time to student progress and changing goals.
As these technologies mature, AI agents are expected to become integral components of holistic student success ecosystems, working alongside human advisors to provide comprehensive support throughout the academic journey.


