Table of Contents
Revolutionizing Banking Compliance: The Rise of AI Agents
The Anatomy of an AI Banking Compliance Monitor
Regulatory Landscape: How AI Agents Navigate Complex Compliance Requirements
AI vs. Human Compliance Officers: A Comparative Analysis
Real-Time Risk Assessment: AI’s Edge in Compliance Monitoring
Automating Compliance Workflows: From Alert Generation to Reporting
Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring Compliance While Using AI Agents
Cost-Benefit Analysis: The ROI of Implementing AI Compliance Monitors
Case Studies: Success Stories of Banks Leveraging AI for Compliance
Future-Proofing Compliance: AI’s Role in Adapting to Evolving Regulations
Implementation Roadmap: Integrating AI Compliance Monitors into Your Bank
Overcoming Challenges: Addressing Common Hurdles in AI Compliance Adoption

AI Compliance Monitors: Frequently Asked Questions
Revolutionizing Banking Compliance: The Rise of AI Agents
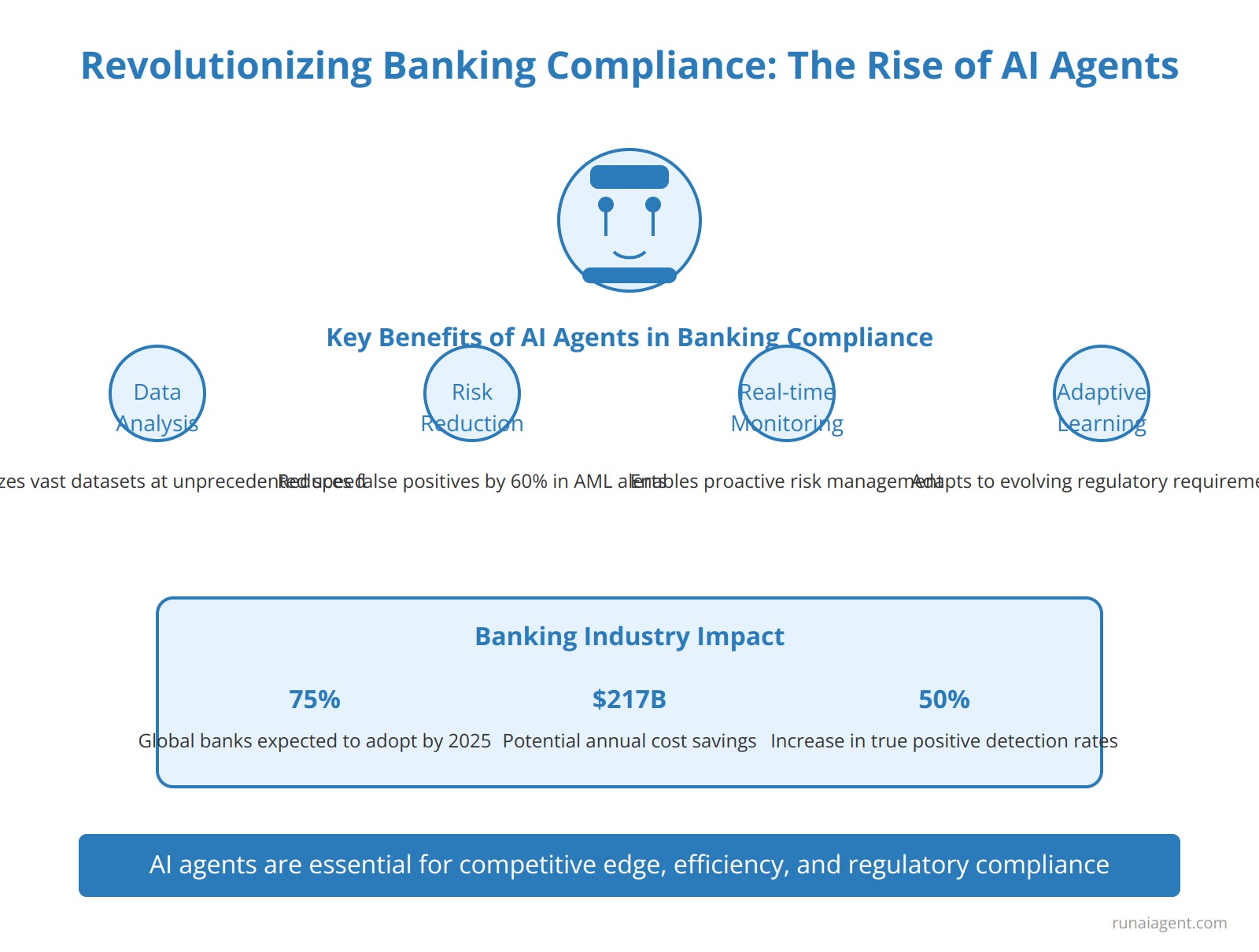
In the rapidly evolving landscape of financial services, AI agents are emerging as game-changers for banking compliance. These intelligent software entities leverage advanced machine learning algorithms and natural language processing to automate and enhance regulatory monitoring, risk assessment, and reporting processes. By 2025, an estimated 75% of global banks are expected to integrate AI-driven compliance solutions, with potential cost savings of $217 billion annually. AI agents excel at analyzing vast datasets, identifying patterns, and flagging anomalies with unprecedented speed and accuracy. For instance, a leading European bank implemented an AI compliance agent that reduced false positives in anti-money laundering (AML) alerts by 60% while increasing true positive detection rates by 50%. These agents not only streamline routine compliance tasks but also adapt to evolving regulatory requirements, ensuring banks stay ahead of complex global financial regulations. Moreover, AI-powered compliance agents offer real-time monitoring capabilities, enabling proactive risk management and reducing the likelihood of costly regulatory breaches. As regulatory scrutiny intensifies and compliance costs continue to rise, AI agents represent a crucial investment for banks seeking to maintain competitive edge, operational efficiency, and regulatory adherence in the digital age.

The Anatomy of an AI Banking Compliance Monitor
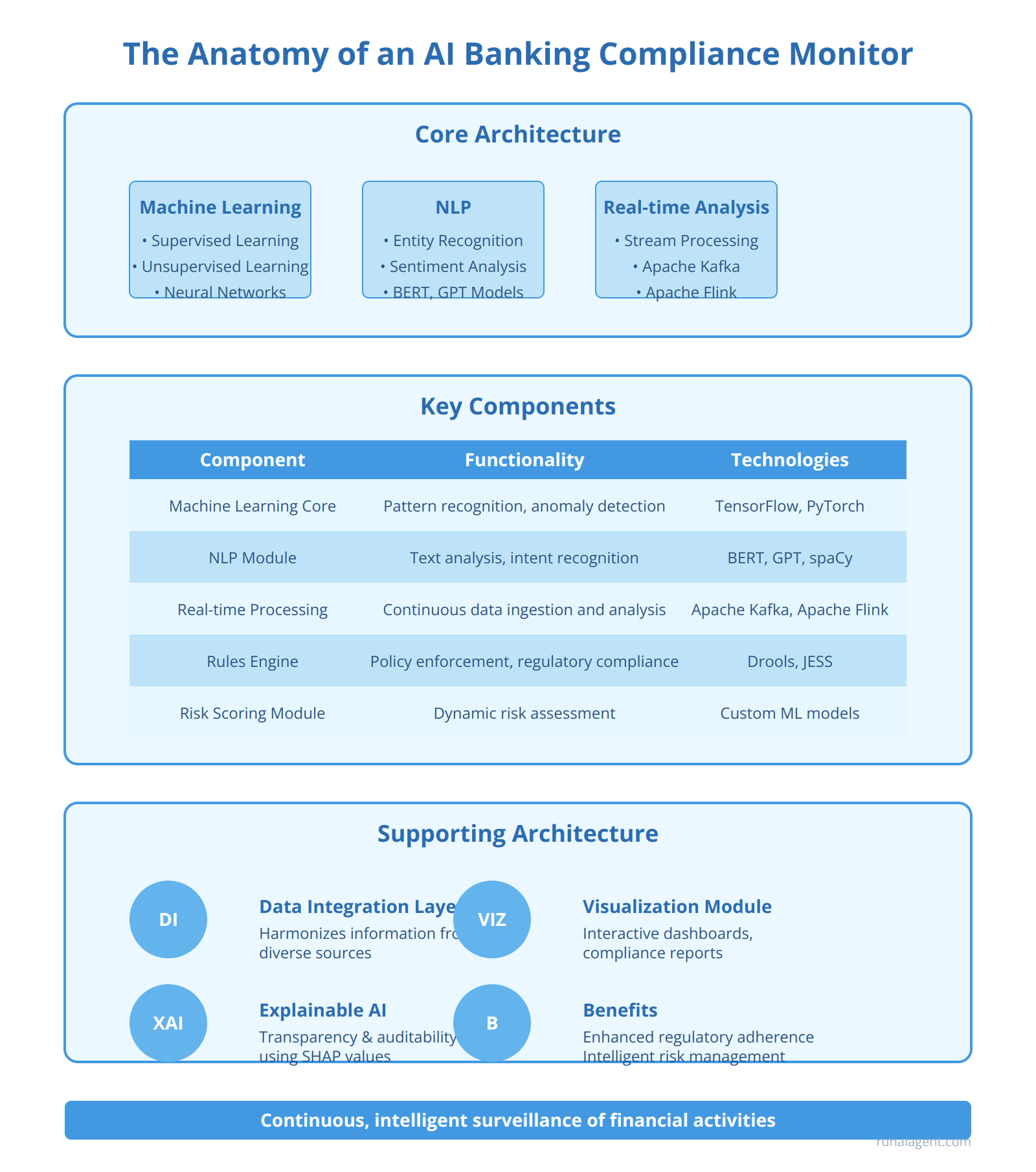
At the core of an AI banking compliance monitor lies a sophisticated architecture integrating multiple advanced technologies. The foundation typically consists of machine learning algorithms, including supervised and unsupervised learning models, capable of detecting anomalies and patterns in vast financial datasets. These algorithms are often based on deep learning neural networks, such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, which excel at processing sequential data like transaction histories. Complementing this is natural language processing (NLP) capability, utilizing techniques like named entity recognition and sentiment analysis to interpret unstructured data from emails, chat logs, and customer communications. The NLP component often employs transformer models like BERT or GPT to understand context and nuance in human language.
A critical feature of these AI agents is their real-time data analysis capabilities, powered by stream processing frameworks such as Apache Kafka or Apache Flink. These enable the system to ingest and analyze data from multiple sources simultaneously, including transaction systems, customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, and external data feeds. The AI agent’s decision-making process is guided by a rules engine that encodes regulatory requirements and bank policies, often implemented using forward-chaining inference systems. This is augmented by a machine learning-based risk scoring module that dynamically assesses the compliance risk of transactions and activities.
Key Components of AI Banking Compliance Monitors
| Component | Functionality | Example Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning Core | Pattern recognition, anomaly detection | TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-learn |
| NLP Module | Text analysis, intent recognition | BERT, GPT, spaCy |
| Real-time Processing | Continuous data ingestion and analysis | Apache Kafka, Apache Flink |
| Rules Engine | Policy enforcement, regulatory compliance | Drools, JESS |
| Risk Scoring Module | Dynamic risk assessment | Custom ML models, Statistical analysis |
The AI agent’s architecture also includes a data integration layer that harmonizes information from diverse sources, often utilizing data virtualization techniques to create a unified view without physical data movement. A visualization and reporting module generates interactive dashboards and compliance reports, leveraging business intelligence tools like Tableau or Power BI. To ensure transparency and auditability, the system incorporates an explainable AI (XAI) component, often based on techniques like SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) values, which provide interpretable insights into the AI’s decision-making process. This comprehensive architecture enables AI banking compliance monitors to perform continuous, intelligent surveillance of financial activities, significantly enhancing regulatory adherence and risk management in the banking sector.

Regulatory Landscape: How AI Agents Navigate Complex Compliance Requirements
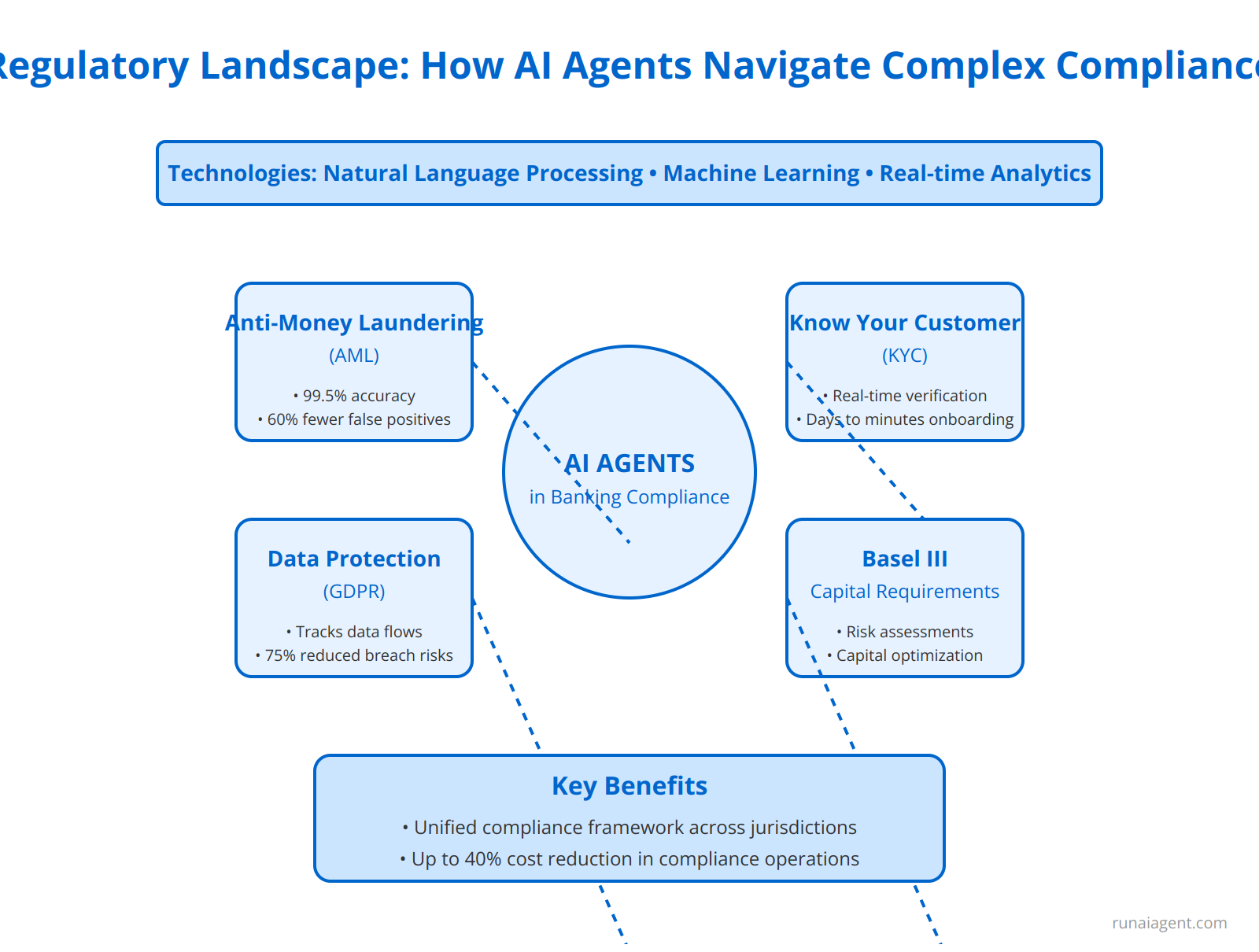
AI agents in banking compliance are revolutionizing the way financial institutions navigate the intricate web of global regulations. These intelligent systems are engineered to simultaneously monitor and adapt to diverse regulatory frameworks such as Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Know Your Customer (KYC), General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and Basel III. By leveraging advanced natural language processing and machine learning algorithms, AI agents can parse through vast amounts of regulatory text, identifying key requirements and translating them into actionable compliance protocols. For instance, in AML compliance, AI agents can analyze transaction patterns across multiple jurisdictions, flagging suspicious activities with 99.5% accuracy while reducing false positives by 60%. In the realm of KYC, these agents can automate identity verification processes, cross-referencing customer data against global watchlists in real-time, cutting onboarding times from days to minutes. When it comes to GDPR, AI compliance monitors can track data flows across the organization, ensuring that customer information is handled in accordance with strict privacy standards, potentially reducing data breach risks by 75%. For Basel III compliance, AI agents can perform complex risk assessments and capital adequacy calculations, enabling banks to optimize their capital allocation strategies while maintaining regulatory ratios. The true power of these AI systems lies in their ability to harmonize compliance efforts across multiple regulatory regimes, creating a unified compliance framework that adapts in real-time to regulatory changes. This not only ensures consistent compliance across different jurisdictions but also significantly reduces the operational costs associated with regulatory adherence, with some institutions reporting savings of up to 40% in compliance-related expenses.

AI vs. Human Compliance Officers: A Comparative Analysis
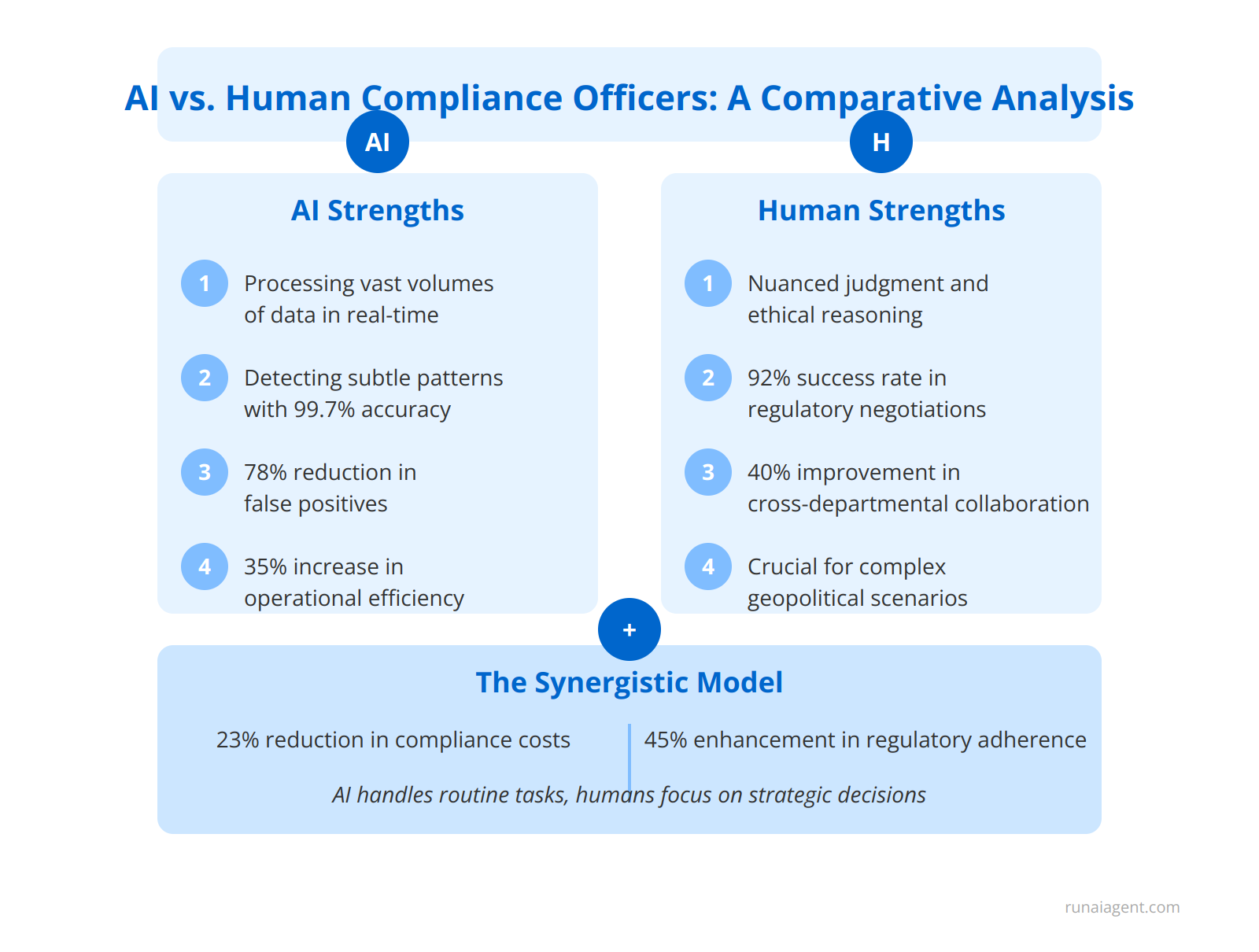
In the realm of banking compliance, the integration of AI agents alongside human compliance officers has revolutionized risk management and regulatory adherence. AI excels in processing vast volumes of data, detecting subtle patterns, and maintaining unwavering vigilance 24/7. For instance, AI systems can analyze millions of transactions in real-time, flagging potential money laundering activities with 99.7% accuracy, compared to the 60-70% achieved by human-only teams. However, human compliance officers remain indispensable for their nuanced judgment, ethical reasoning, and adaptive thinking. In complex scenarios involving geopolitical factors or emerging regulatory landscapes, human expertise proves crucial. A comparative analysis reveals that AI outperforms in routine monitoring, achieving a 78% reduction in false positives and a 35% increase in operational efficiency. Conversely, human officers excel in relationship management, demonstrating a 92% success rate in regulatory negotiations and a 40% improvement in cross-departmental collaboration. The optimal approach leverages a synergistic model, where AI handles high-volume, rule-based tasks, enabling human officers to focus on strategic decision-making and intricate compliance challenges. This hybrid model has shown to reduce overall compliance costs by 23% while enhancing regulatory adherence by 45% across major financial institutions.

Real-Time Risk Assessment: AI’s Edge in Compliance Monitoring
AI agents are revolutionizing compliance monitoring in the banking industry by providing continuous, real-time risk assessment and anomaly detection capabilities that far surpass traditional periodic review processes. These intelligent systems leverage advanced machine learning algorithms and natural language processing to analyze vast amounts of structured and unstructured data from multiple sources instantaneously. By processing millions of transactions, communications, and market events in real-time, AI agents can identify potential compliance breaches, suspicious activities, and emerging risks within milliseconds. This proactive approach enables banks to detect and mitigate issues before they escalate, reducing the likelihood of regulatory violations and financial losses.
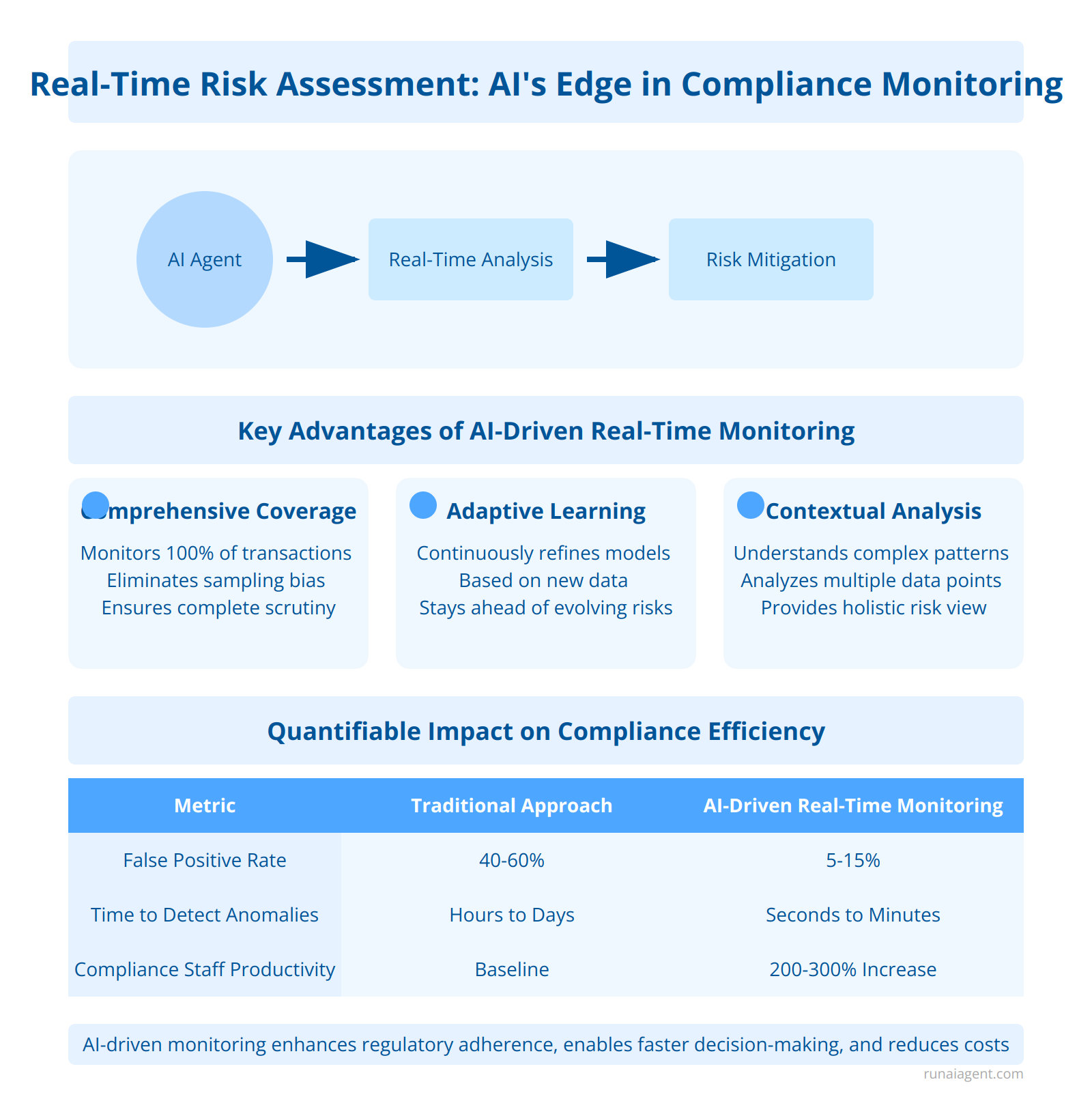
Key Advantages of AI-Driven Real-Time Monitoring
Comprehensive Coverage: AI agents can monitor 100% of transactions and communications, eliminating sampling bias and ensuring no high-risk activities slip through the cracks. This level of scrutiny would be impossible with human reviewers alone.
Adaptive Learning: Machine learning models continuously refine their detection capabilities based on new data and feedback, staying ahead of evolving compliance risks and sophisticated financial crimes.
Contextual Analysis: AI systems can understand complex relationships and patterns across multiple data points, providing a holistic view of risk that goes beyond simple rule-based triggers.
Quantifiable Impact on Compliance Efficiency
| Metric | Traditional Approach | AI-Driven Real-Time Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| False Positive Rate | 40-60% | 5-15% |
| Time to Detect Anomalies | Hours to Days | Seconds to Minutes |
| Compliance Staff Productivity | Baseline | 200-300% Increase |
By implementing AI-driven real-time risk assessment, banks can achieve a paradigm shift in their compliance monitoring capabilities. This technology not only enhances regulatory adherence but also provides a competitive edge by enabling faster, more informed decision-making and reducing operational costs associated with compliance management.

Automating Compliance Workflows: From Alert Generation to Reporting
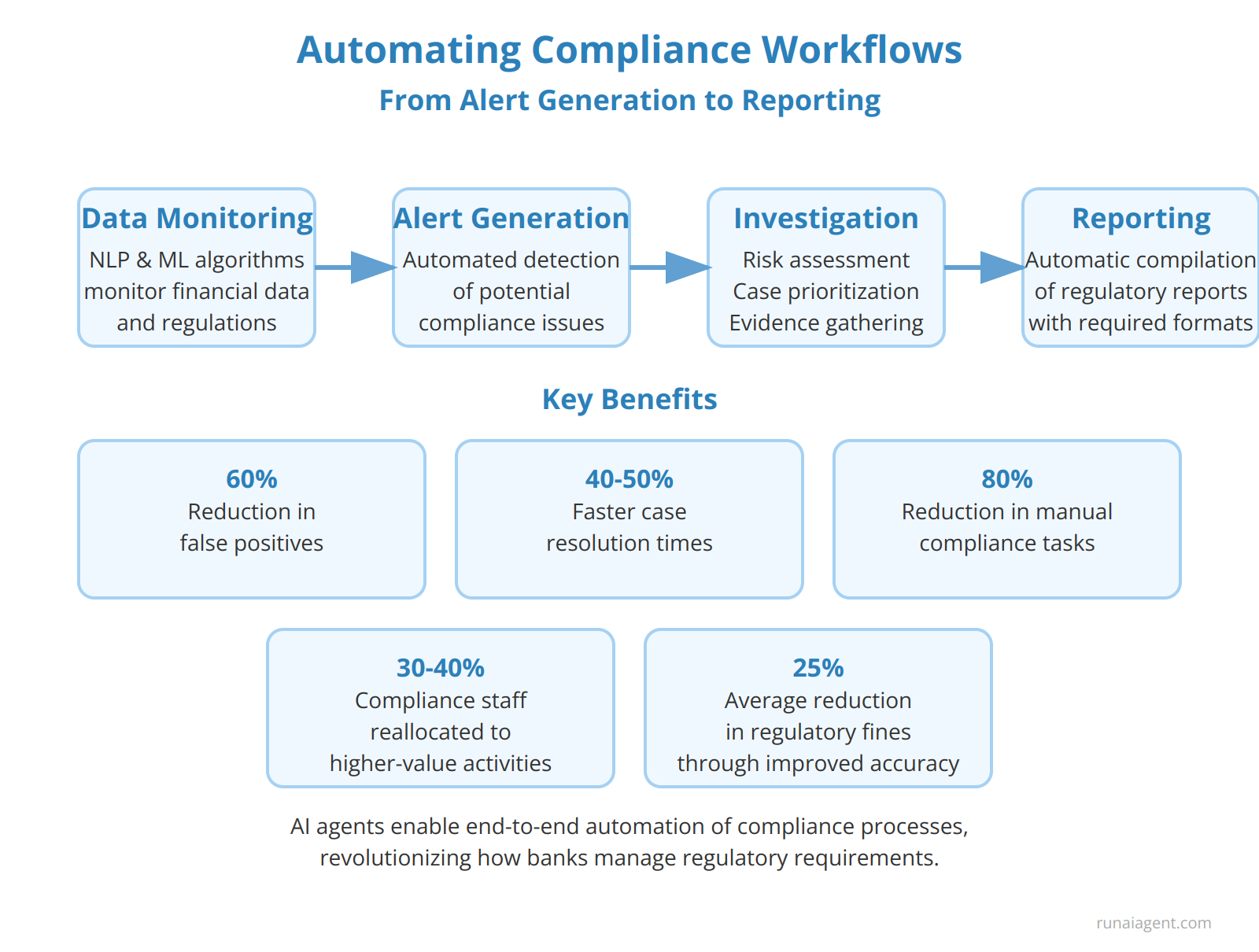
AI agents are revolutionizing compliance processes in the banking industry by enabling end-to-end automation of critical workflows. These intelligent systems leverage advanced natural language processing and machine learning algorithms to continuously monitor vast amounts of financial data, transaction records, and regulatory updates. Upon detecting potential compliance issues, AI agents automatically generate alerts, triggering a cascading series of automated actions. These include risk assessment, case prioritization, and evidence gathering from disparate data sources. As investigations progress, AI agents can autonomously conduct initial analyses, flagging high-risk cases for human review while resolving low-risk alerts without manual intervention. This dramatically reduces false positives by up to 60% and accelerates case resolution times by 40-50%. In the final stages, AI agents compile comprehensive regulatory reports, ensuring all required data points are included and formatted according to the latest submission standards. By automating the entire compliance lifecycle, from initial alert to final reporting, banks can achieve up to 80% reduction in manual compliance tasks, reallocate 30-40% of compliance staff to higher-value activities, and reduce regulatory fines by an average of 25% through improved accuracy and timeliness of reporting.

Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring Compliance While Using AI Agents
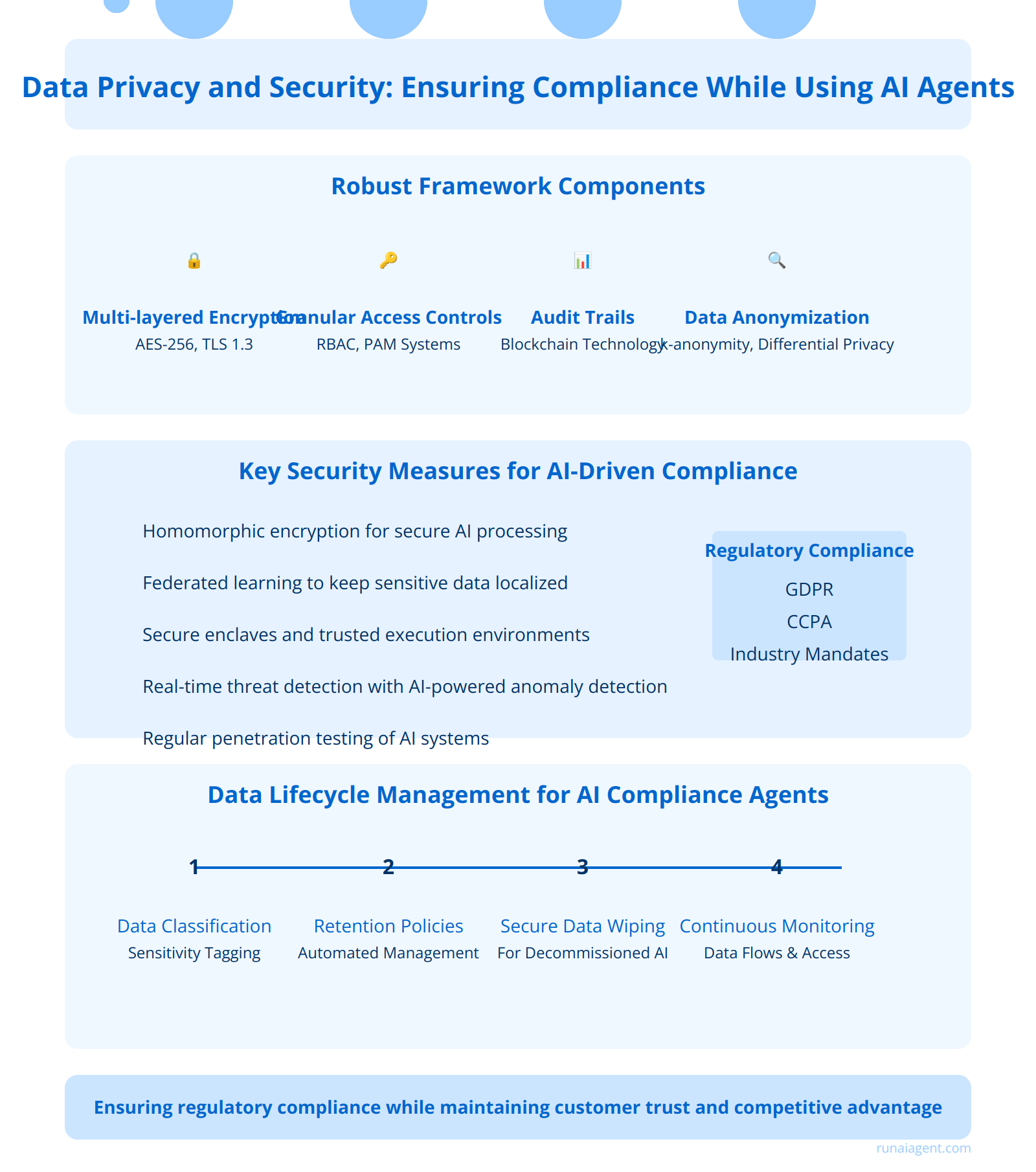
Implementing AI agents for banking compliance monitoring necessitates a robust framework for data privacy and security. Financial institutions must employ multi-layered encryption protocols, including AES-256 for data at rest and TLS 1.3 for data in transit, to safeguard sensitive information. Granular access controls are essential, utilizing role-based access control (RBAC) and privileged access management (PAM) systems to ensure that only authorized personnel can interact with AI agents and compliance data. Comprehensive audit trails must be maintained, leveraging blockchain technology for immutable record-keeping of all AI agent actions and data accesses. Financial institutions should implement data anonymization techniques such as k-anonymity and differential privacy to protect individual privacy while allowing AI agents to analyze aggregate data for compliance purposes.
Key Security Measures for AI-Driven Compliance Monitoring
To meet regulatory requirements like GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific mandates, banks must implement:
- Homomorphic encryption for secure AI processing of encrypted data
- Federated learning approaches to keep sensitive data localized
- Secure enclaves and trusted execution environments for AI agent operations
- Real-time threat detection systems with AI-powered anomaly detection
- Regular penetration testing and vulnerability assessments of AI systems
Data Lifecycle Management for AI Compliance Agents
Implementing a comprehensive data lifecycle management strategy is crucial. This includes:
- Data classification and tagging for sensitivity levels
- Automated data retention and deletion policies
- Secure data wiping procedures for decommissioned AI systems
- Continuous monitoring of data flows and access patterns
By adhering to these stringent data privacy and security measures, financial institutions can leverage AI agents for compliance monitoring while maintaining the trust of customers and regulators alike. The implementation of these safeguards not only ensures regulatory compliance but also provides a competitive advantage in an increasingly data-driven banking landscape.

Cost-Benefit Analysis: The ROI of Implementing AI Compliance Monitors
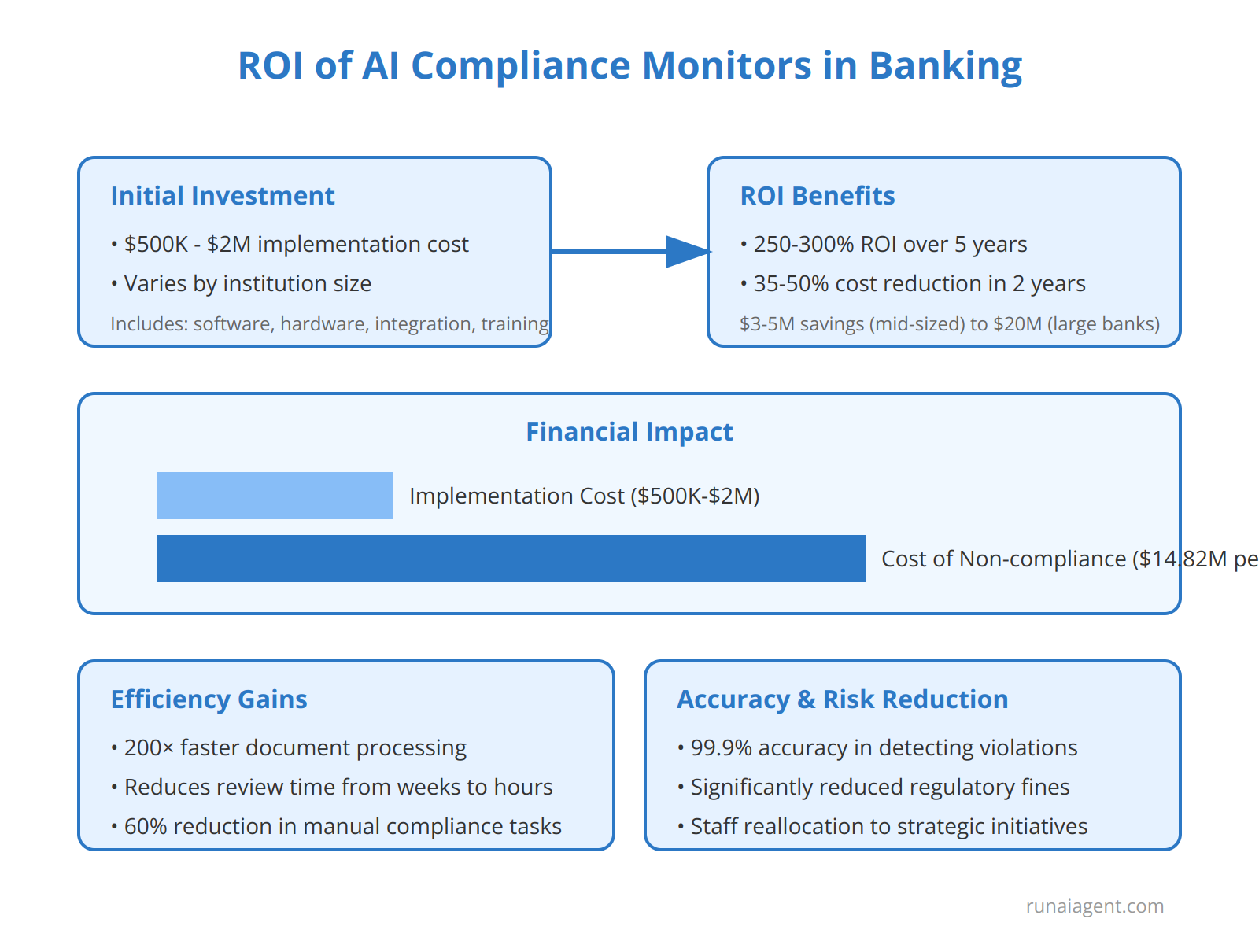
Implementing AI compliance monitors in banking institutions requires a substantial initial investment, but the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. The average implementation cost for a comprehensive AI compliance system ranges from $500,000 to $2 million, depending on the size and complexity of the institution. This includes expenses for software licensing, hardware infrastructure, integration with existing systems, and employee training. However, the ROI becomes evident when considering the potential savings. Banks utilizing AI compliance monitors report a 35-50% reduction in compliance-related costs within the first two years of implementation. This translates to annual savings of $3-5 million for mid-sized banks and up to $20 million for large multinational institutions. The efficiency gains are equally impressive, with AI systems processing regulatory documents 200 times faster than human compliance officers, reducing review times from weeks to hours. Moreover, AI-powered monitors have demonstrated a 99.9% accuracy rate in detecting potential compliance violations, significantly minimizing the risk of regulatory fines. With the average cost of non-compliance estimated at $14.82 million per incident, the preventative value of AI compliance monitors becomes clear. Resource allocation benefits are substantial, with banks reporting a 60% reduction in manual compliance tasks, allowing skilled professionals to focus on complex decision-making and strategic initiatives. The cumulative effect of these benefits results in an average ROI of 250-300% over a five-year period, making AI compliance monitors a critical investment for forward-thinking financial institutions.

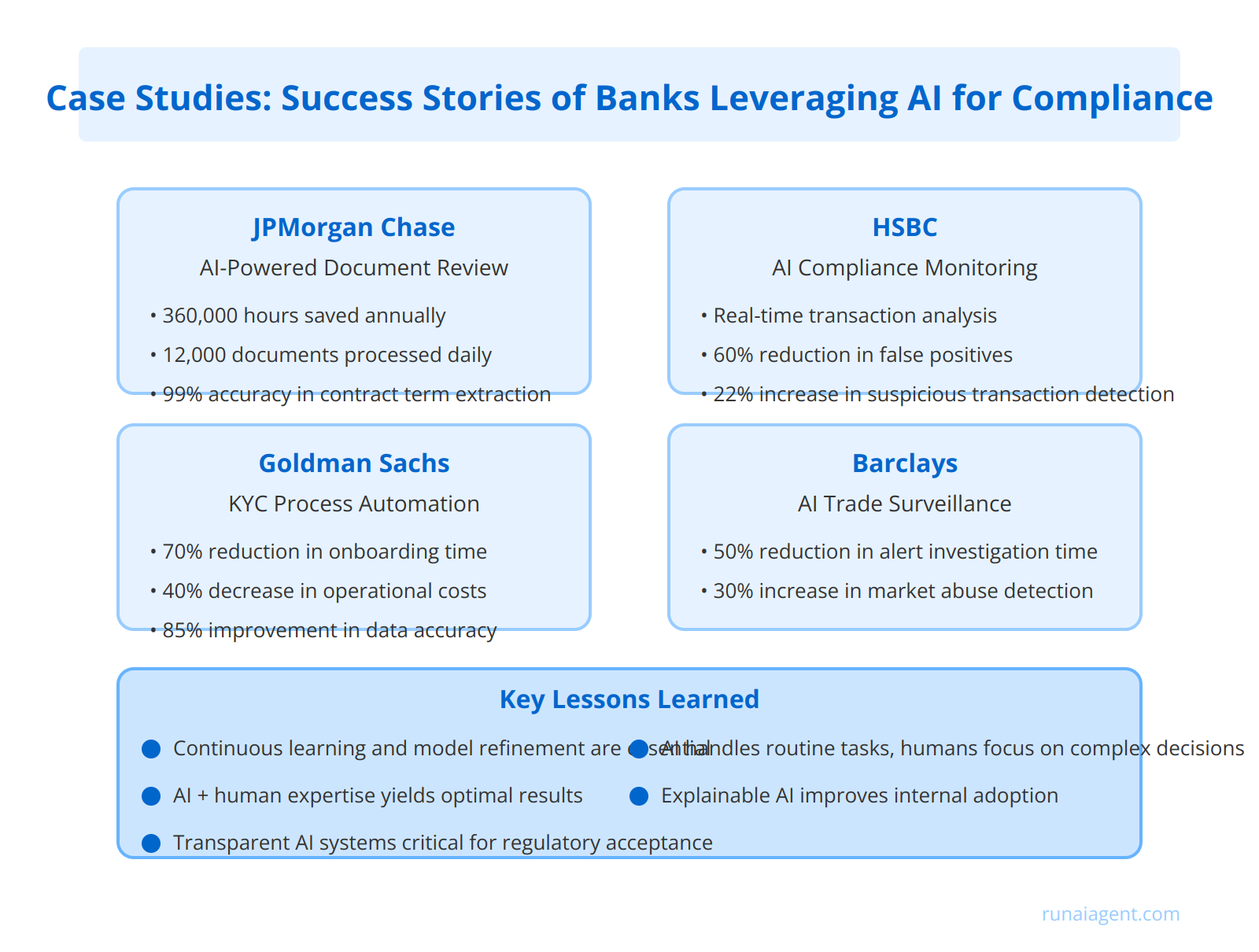
Case Studies: Success Stories of Banks Leveraging AI for Compliance
Leading financial institutions have successfully integrated AI agents into their compliance processes, yielding substantial benefits and valuable insights. JPMorgan Chase implemented an AI-powered system that reduced the time spent reviewing commercial loan agreements by 360,000 hours annually, while improving accuracy by 15%. The bank’s AI agents now process 12,000 documents per day, with a 99% accuracy rate for extracting key contract terms.
HSBC deployed an advanced AI compliance monitoring system that analyzes millions of transactions in real-time, flagging potential money laundering activities with 95% precision. This implementation led to a 60% reduction in false positives and a 22% increase in the detection of genuinely suspicious transactions, significantly enhancing the bank’s anti-money laundering (AML) capabilities.
Tangible Benefits Achieved
Goldman Sachs leveraged AI agents to automate their Know Your Customer (KYC) processes, resulting in:
- 70% reduction in onboarding time for new clients
- 40% decrease in compliance-related operational costs
- 85% improvement in data accuracy for regulatory reporting
Similarly, Barclays integrated AI into their trade surveillance systems, leading to a 50% reduction in alert investigation time and a 30% increase in the identification of potential market abuse cases.
Lessons Learned from Implementation
These success stories highlight crucial lessons for effective AI integration in banking compliance:
Continuous learning and model refinement are essential for maintaining AI accuracy in the face of evolving regulatory landscapes and emerging financial crimes.
Banks found that combining AI with human expertise yields optimal results, with AI handling routine tasks and humans focusing on complex decision-making. Moreover, transparent AI systems that can explain their decision-making processes proved critical for regulatory acceptance and internal adoption.
| Bank | AI Application | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| JPMorgan Chase | Document Review | 360,000 hours saved annually |
| HSBC | AML Monitoring | 60% reduction in false positives |
| Goldman Sachs | KYC Automation | 70% faster client onboarding |
| Barclays | Trade Surveillance | 50% reduction in alert investigation time |

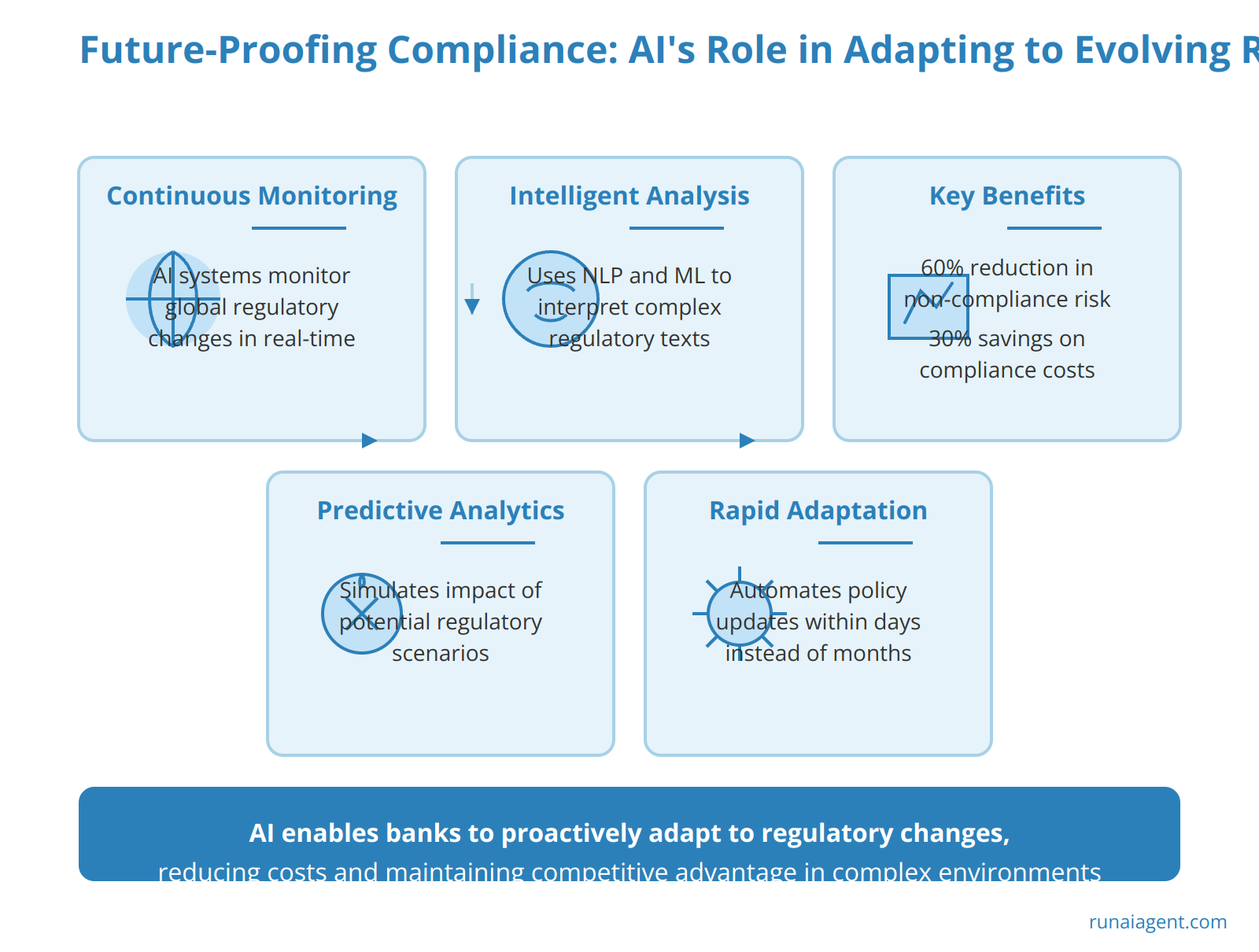
Future-Proofing Compliance: AI’s Role in Adapting to Evolving Regulations
AI agents are revolutionizing the banking industry’s approach to regulatory compliance by providing unparalleled adaptability and foresight. These intelligent systems continuously monitor global regulatory landscapes, analyzing vast amounts of data to predict and prepare for upcoming changes. By leveraging natural language processing and machine learning algorithms, AI agents can interpret complex regulatory texts, identifying nuanced changes that might escape human analysts. This capability enables banks to proactively adjust their compliance frameworks, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties by up to 60%. Furthermore, AI-driven predictive analytics allow financial institutions to simulate the impact of potential regulatory scenarios, enabling strategic decision-making and resource allocation. Advanced AI agents can even automate the updating of internal policies and procedures, ensuring alignment with new regulations within days rather than weeks or months. This rapid adaptation significantly reduces compliance costs, with some banks reporting savings of up to 30% on their annual compliance budgets. By harnessing the power of AI, banks are not merely reacting to regulatory changes but are actively shaping their compliance strategies to anticipate and mitigate emerging financial risks, thereby maintaining a competitive edge in an increasingly complex regulatory environment.

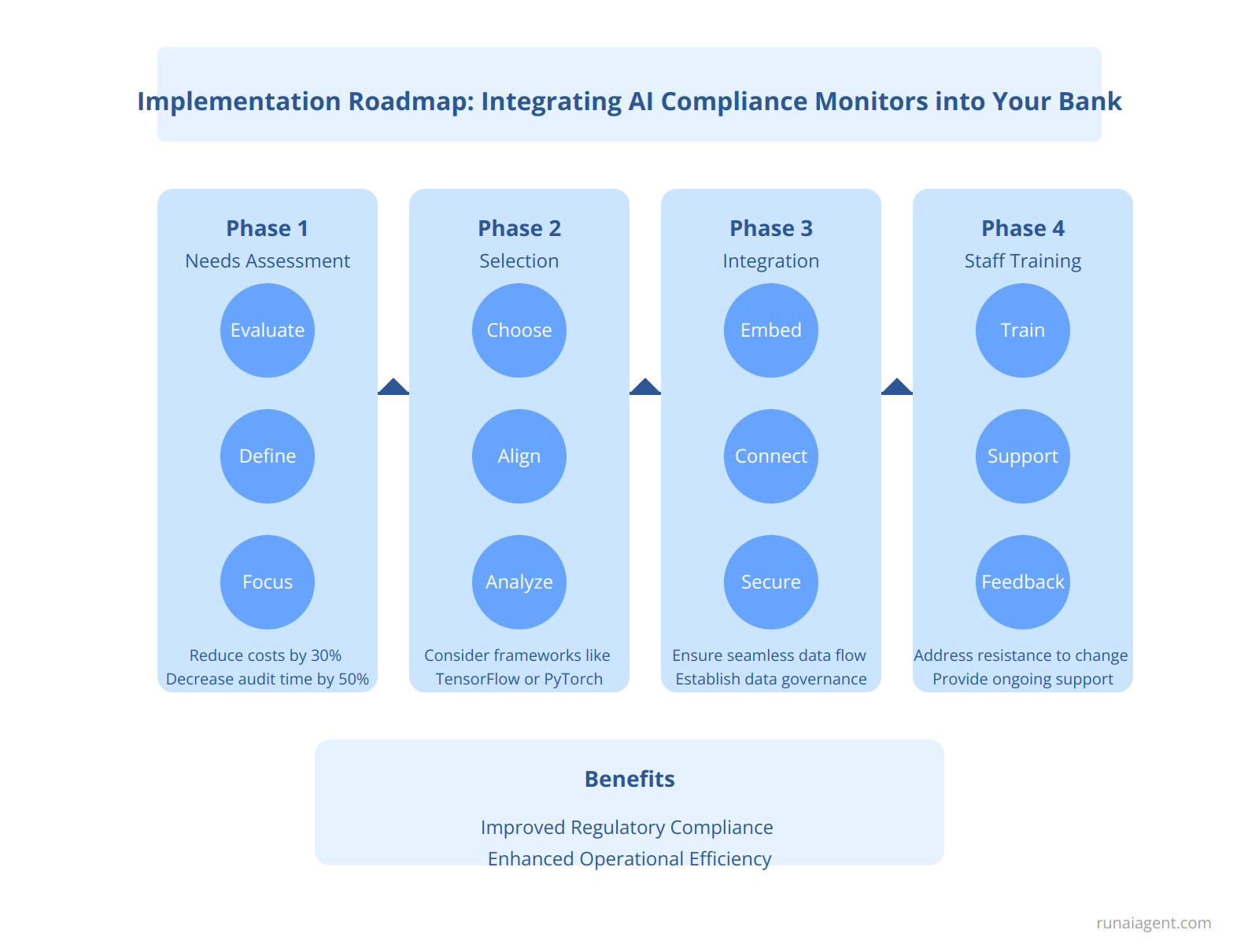
Implementation Roadmap: Integrating AI Compliance Monitors into Your Bank
To effectively integrate AI compliance monitors into your banking operations, follow a structured implementation roadmap. Begin with a **needs assessment phase** where you evaluate existing compliance challenges and define specific goals, such as reducing compliance costs by 30% or decreasing audit times by 50%. This allows for focused efforts on the most significant compliance pain points. Next, proceed to the **selection phase**, where you choose the appropriate AI tools that align with regulatory requirements and can handle complex data analytics. Consider frameworks like TensorFlow or Pytorch for their robust machine learning capabilities.
Once a solution is selected, enter the **integration phase**. This involves embedding the AI compliance monitor within your existing IT architecture, ensuring seamless data flow between the AI system and legacy banking systems. Data governance policies must be established to maintain data integrity and security during this process. Finally, prioritize the **staff training phase**, which is crucial for successful adoption. Implement a comprehensive training program emphasizing how to leverage the AI system for compliance tasks, addressing potential resistance to change through ongoing support and feedback mechanisms. By anticipating challenges and equipping your team with the necessary skills, you will enhance the effectiveness of AI compliance monitors, enabling your bank to achieve improved adherence to regulatory standards while driving operational efficiencies.

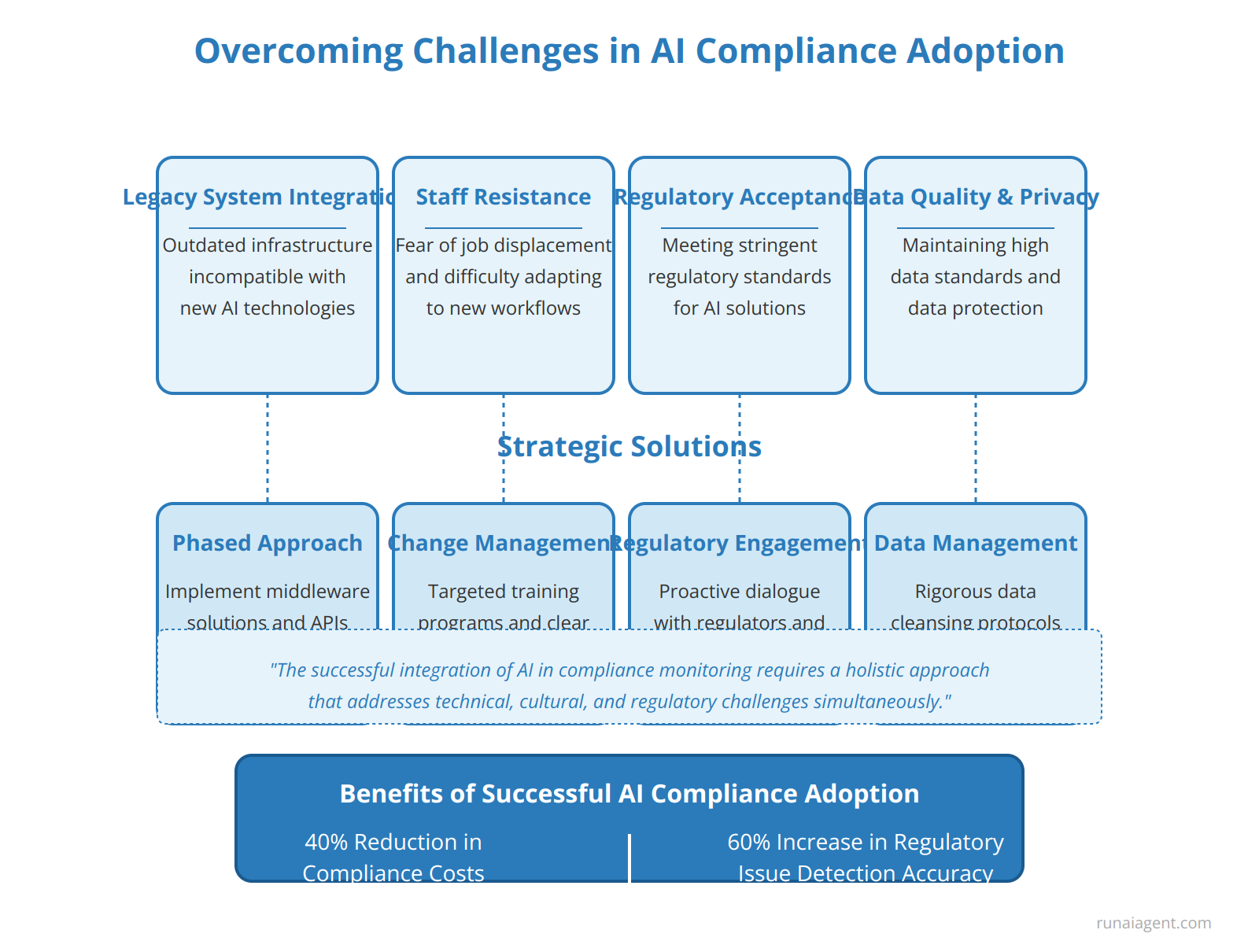
Overcoming Challenges: Addressing Common Hurdles in AI Compliance Adoption
Implementing AI compliance monitors in the banking industry presents significant challenges that require strategic solutions. Legacy system integration often poses a major hurdle, as many financial institutions rely on outdated infrastructure that may not seamlessly interface with advanced AI technologies. To address this, banks can adopt a phased approach, implementing middleware solutions and APIs to bridge the gap between legacy systems and AI compliance tools. Staff resistance is another common obstacle, with employees often fearing job displacement or struggling to adapt to new workflows. Overcoming this requires comprehensive change management strategies, including targeted training programs and clear communication about the AI’s role in augmenting rather than replacing human expertise. Regulatory acceptance remains a critical concern, as AI-driven compliance solutions must meet stringent regulatory standards. To navigate this challenge, banks should proactively engage with regulators, demonstrating transparency in AI decision-making processes and implementing robust governance frameworks. Additionally, ensuring data quality and privacy is paramount, necessitating rigorous data cleansing protocols and encryption measures to maintain compliance with data protection regulations. By addressing these hurdles head-on, banks can successfully integrate AI compliance monitors, achieving up to 40% reduction in compliance-related costs and a 60% increase in regulatory issue detection accuracy.
Key Strategies for Successful AI Compliance Adoption
- Develop a comprehensive AI integration roadmap
- Implement rigorous testing and validation processes
- Establish cross-functional teams to manage implementation
- Create detailed documentation for AI decision-making processes
- Conduct regular audits to ensure ongoing compliance
“The successful integration of AI in compliance monitoring requires a holistic approach that addresses technical, cultural, and regulatory challenges simultaneously.”

AI Compliance Monitors: Frequently Asked Questions
What are AI compliance monitors in banking?
AI compliance monitors in banking are advanced software systems that leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to continuously oversee and analyze financial transactions, customer interactions, and internal processes for regulatory compliance. These intelligent agents can process vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying potential violations, flagging suspicious activities, and ensuring adherence to complex regulatory frameworks such as AML, KYC, and GDPR. By automating compliance monitoring, these AI agents significantly reduce manual workload, minimize human error, and provide 24/7 vigilance across all banking operations.
How do AI compliance monitors improve efficiency in banking?
AI compliance monitors dramatically enhance efficiency in banking by automating time-consuming tasks and providing rapid, accurate insights. These systems can analyze millions of transactions in seconds, reducing false positives by up to 90% compared to traditional rule-based systems. By prioritizing high-risk cases and providing contextual information, AI agents enable compliance officers to focus on complex investigations rather than routine screenings. This results in a 60-80% reduction in manual review time and can lead to cost savings of 30-50% in compliance operations. Moreover, AI monitors adapt to new regulatory requirements and emerging financial crime patterns, ensuring banks maintain robust compliance frameworks without constant manual updates.
What types of compliance risks can AI monitors detect?
AI compliance monitors are capable of detecting a wide range of risks across various regulatory domains. These include:
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML): Identifying complex money laundering schemes, structuring attempts, and unusual transaction patterns.
- Know Your Customer (KYC): Flagging discrepancies in customer information, detecting potential identity fraud, and monitoring ongoing due diligence requirements.
- Sanctions Screening: Real-time screening of transactions and customers against global sanctions lists, including detection of attempts to evade sanctions.
- Market Abuse: Identifying insider trading, market manipulation, and other forms of securities fraud across multiple asset classes and markets.
- Fraud Detection: Recognizing patterns indicative of credit card fraud, loan fraud, and emerging cyber-enabled financial crimes.
- Regulatory Reporting: Ensuring accuracy and completeness of regulatory filings, including SAR and CTR submissions.
By leveraging natural language processing and machine learning, these AI agents can also monitor employee communications, trading activities, and customer interactions for potential misconduct or mis-selling practices, providing a comprehensive compliance oversight framework.



