Table of Contents
The Rise of AI Agents in CAD Drafting: Revolutionizing Engineering and Manufacturing
Understanding AI Agents: The New Powerhouse in CAD Design
AI vs. Human CAD Drafters: A Comparative Analysis
Implementing AI Agents in Your CAD Workflow: A Step-by-Step Guide
The Economic Impact: Cost-Benefit Analysis of AI Agents in CAD Drafting
Enhancing Precision and Efficiency: How AI Agents Optimize CAD Design
The Future of CAD Drafting: AI Agents and Emerging Technologies

Overcoming Challenges: Addressing Concerns About AI in CAD Drafting
Case Studies: Success Stories of AI Agents in Engineering and Manufacturing

Training and Upskilling: Preparing Your Team for AI-Assisted CAD Drafting
Legal and Ethical Considerations: Navigating the AI Landscape in CAD Design

FAQ: Everything You Need to Know About AI Agents in CAD Drafting
The Rise of AI Agents in CAD Drafting: Revolutionizing Engineering and Manufacturing
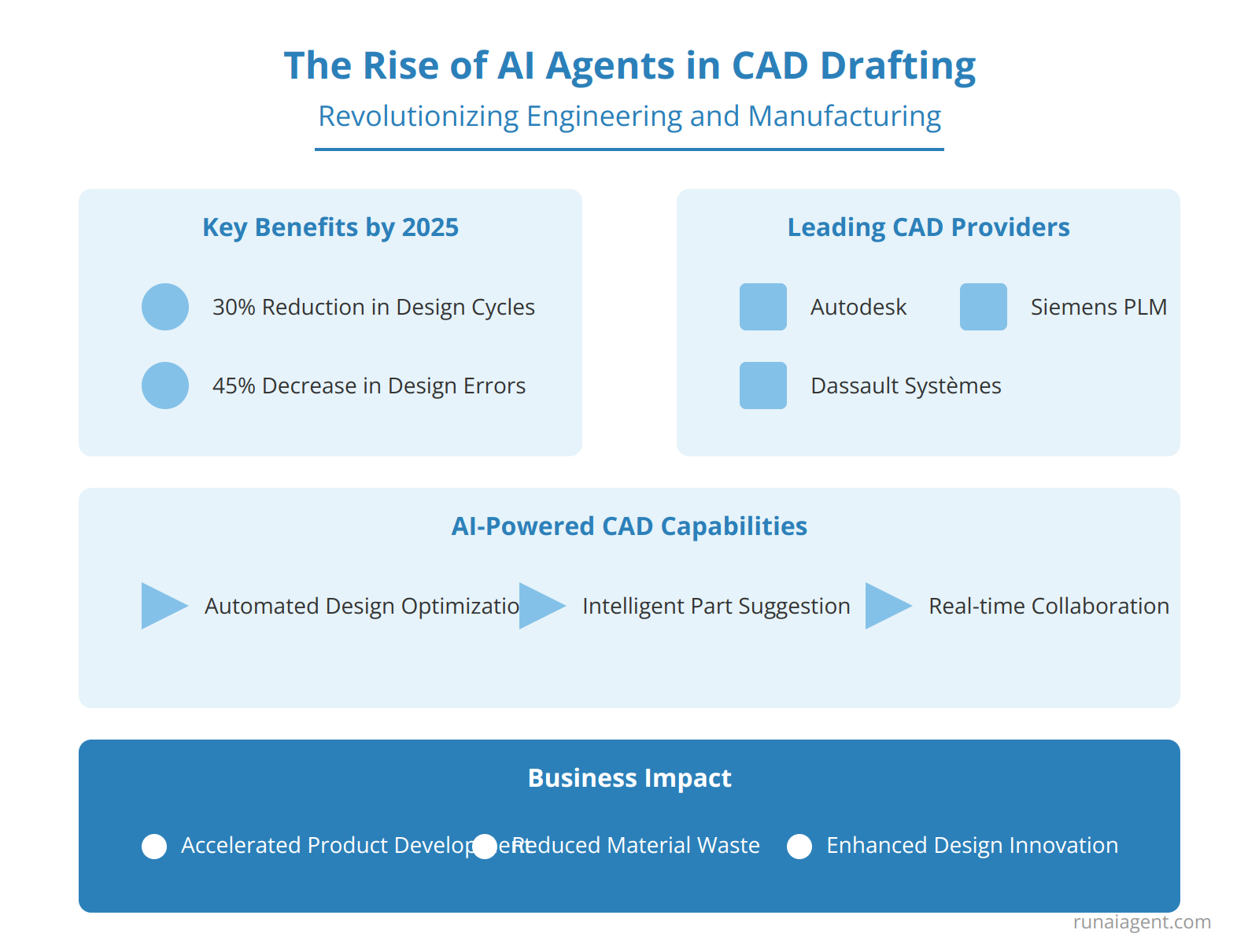
AI agents are transforming Computer-Aided Design (CAD) drafting in the engineering and manufacturing sectors. These intelligent software entities leverage advanced machine learning algorithms, including deep neural networks and reinforcement learning, to automate complex drafting tasks traditionally performed by human designers. By 2025, AI-powered CAD systems are projected to reduce design cycle times by up to 30% and decrease errors by 45%, translating to significant cost savings for businesses. Leading CAD software providers like Autodesk, Dassault Systèmes, and Siemens PLM Software are integrating AI agents into their platforms, enabling features such as automated design optimization, intelligent part suggestion, and real-time collaboration between human designers and AI assistants. These AI agents can analyze vast libraries of existing designs, material properties, and manufacturing constraints to generate optimized 3D models that adhere to specific engineering requirements and industry standards. For business owners in the engineering and manufacturing space, the adoption of AI-driven CAD tools represents a critical competitive advantage, offering the potential to accelerate product development cycles, reduce material waste, and unlock new levels of design innovation.

Understanding AI Agents: The New Powerhouse in CAD Design
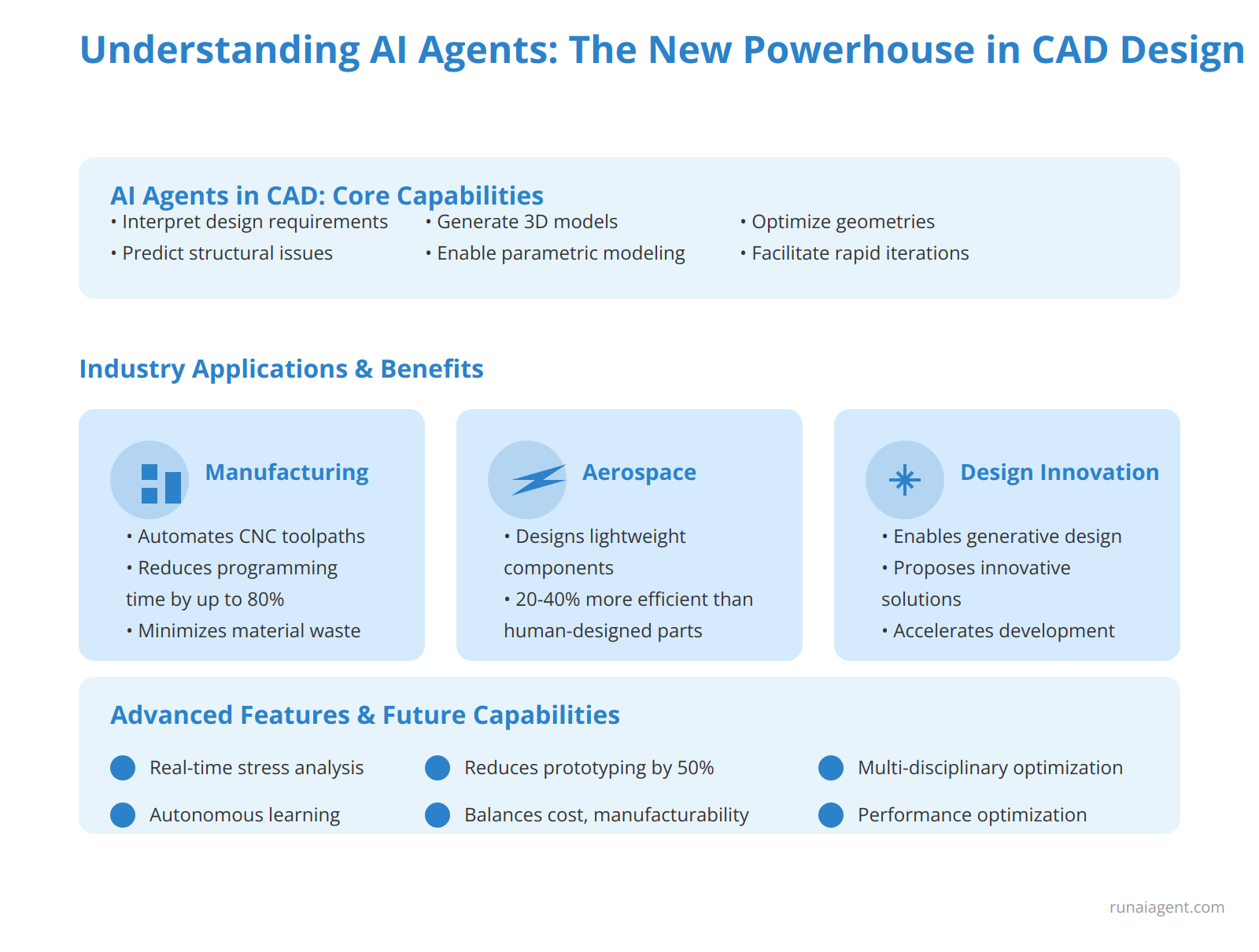
AI agents are transforming Computer-Aided Design (CAD) in engineering and manufacturing by leveraging advanced machine learning algorithms and neural networks to automate complex drafting tasks. These intelligent software entities operate autonomously within CAD environments, continuously learning from user interactions and design patterns to improve their performance. AI agents in CAD systems can interpret design requirements, generate 3D models, optimize geometries, and predict potential structural issues. They excel at parametric modeling, allowing for rapid design iterations and exploration of multiple design variants simultaneously. An AI agent can automatically generate and refine toolpaths for CNC machining, reducing programming time by up to 80% and minimizing material waste. In aerospace applications, AI agents have designed lightweight components that are 20-40% more efficient than human-designed counterparts, while adhering to safety regulations. These agents facilitate generative design processes, proposing innovative solutions that human designers might not consider. By integrating with simulation software, AI agents can perform real-time stress analysis and suggest design modifications, potentially reducing the need for physical prototyping by up to 50%. These agents are increasingly capable of handling multi-disciplinary optimization tasks, balancing factors such as manufacturability, cost, and performance.

AI vs. Human CAD Drafters: A Comparative Analysis
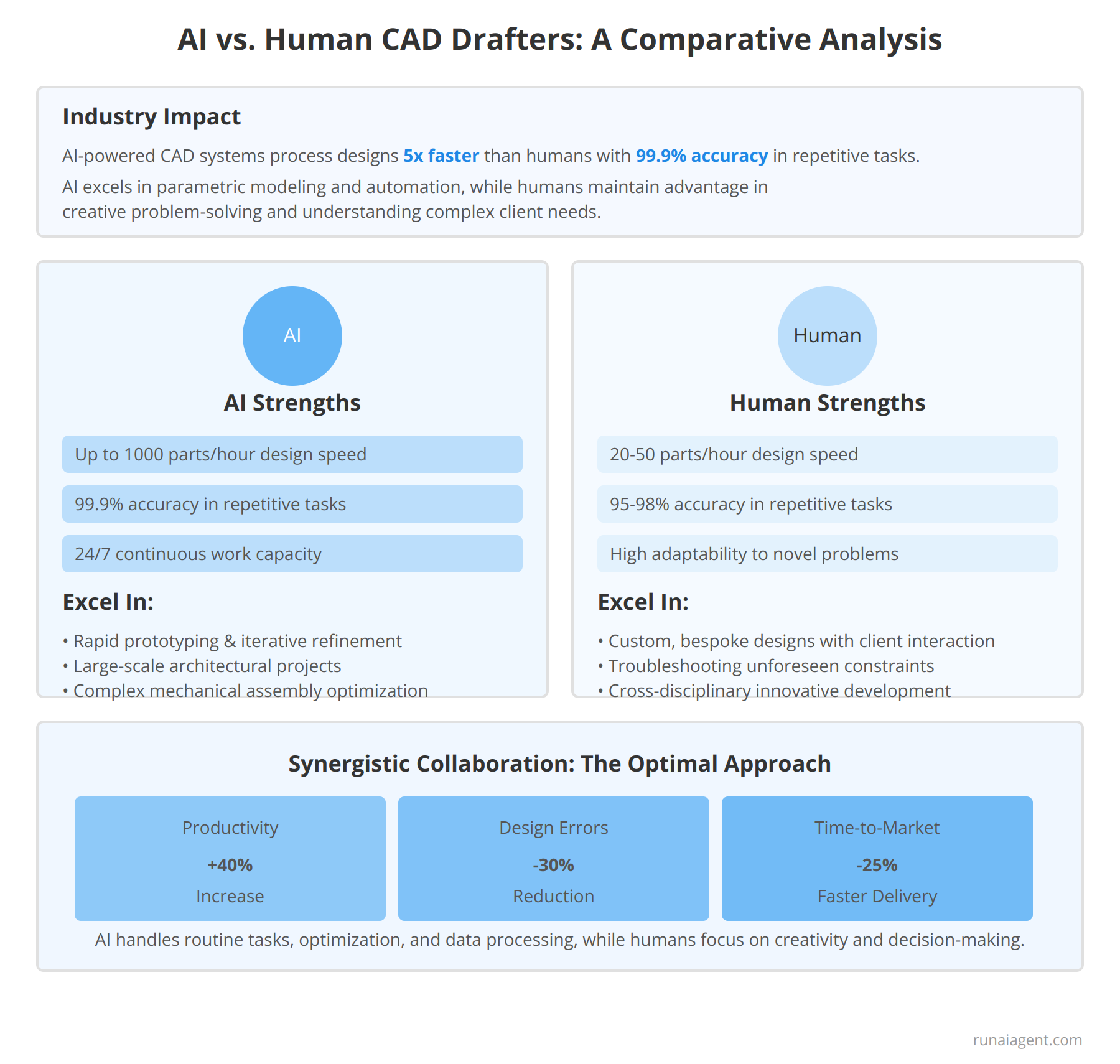
In the engineering and manufacturing industry, the integration of AI agents into Computer-Aided Design (CAD) processes has sparked a paradigm shift. AI-powered CAD systems process complex designs up to 5 times faster than their human counterparts and maintain consistent accuracy rates of 99.9% across repetitive tasks. These AI agents excel in parametric modeling, automating routine design iterations, and rapidly generating multiple design variants based on predefined parameters. However, human CAD drafters retain a crucial edge in creative problem-solving, especially when confronted with novel design challenges that require intuitive understanding of client needs and manufacturing constraints.
Efficiency and Accuracy
AI agents in CAD significantly outperform humans in terms of speed and precision for standardized tasks. They can work continuously without fatigue, completing large-scale projects in a fraction of the time required by human teams. AI-driven generative design tools can explore thousands of design possibilities in hours, a process that would take human drafters weeks or months. However, the accuracy of AI-generated designs is heavily dependent on the quality and comprehensiveness of input data and training datasets.
Creativity and Problem-Solving
Human CAD drafters excel in conceptual design phases, where creativity and out-of-the-box thinking are paramount. They possess the unique ability to interpret vague client requirements, incorporate aesthetic considerations, and anticipate potential issues based on years of experience. AI agents, while adept at optimization within defined parameters, struggle with truly innovative solutions that require a holistic understanding of design principles, manufacturing processes, and market trends.
Scenarios of Excellence
AI agents demonstrate superior performance in:
- Rapid prototyping and iterative design refinement
- Large-scale architectural and infrastructure projects requiring precise calculations
- Optimization of complex mechanical assemblies for weight reduction and performance enhancement
Human expertise remains crucial in:
- Custom, bespoke designs requiring nuanced client interaction
- Troubleshooting and adapting designs to unforeseen manufacturing constraints
- Integrating cross-disciplinary knowledge for innovative product development
Comparative Performance Metrics
| Metric | AI Agents | Human CAD Drafters |
|---|---|---|
| Design Speed (standard components) | Up to 1000 parts/hour | 20-50 parts/hour |
| Accuracy in Repetitive Tasks | 99.9% | 95-98% |
| Novel Problem-Solving Capability | Limited to training data | High adaptability |
| Continuous Work Capacity | 24/7 | 8-10 hours/day |
The optimal approach in modern CAD workflows involves a synergistic collaboration between AI agents and human drafters. By leveraging AI for routine tasks, data processing, and design optimization, human experts can focus on high-value activities that require creativity, contextual understanding, and strategic decision-making. This hybrid model has shown to increase overall productivity by up to 40% in leading engineering firms, while simultaneously reducing design errors by 30% and accelerating time-to-market for new products by an average of 25%.

Implementing AI Agents in Your CAD Workflow: A Step-by-Step Guide
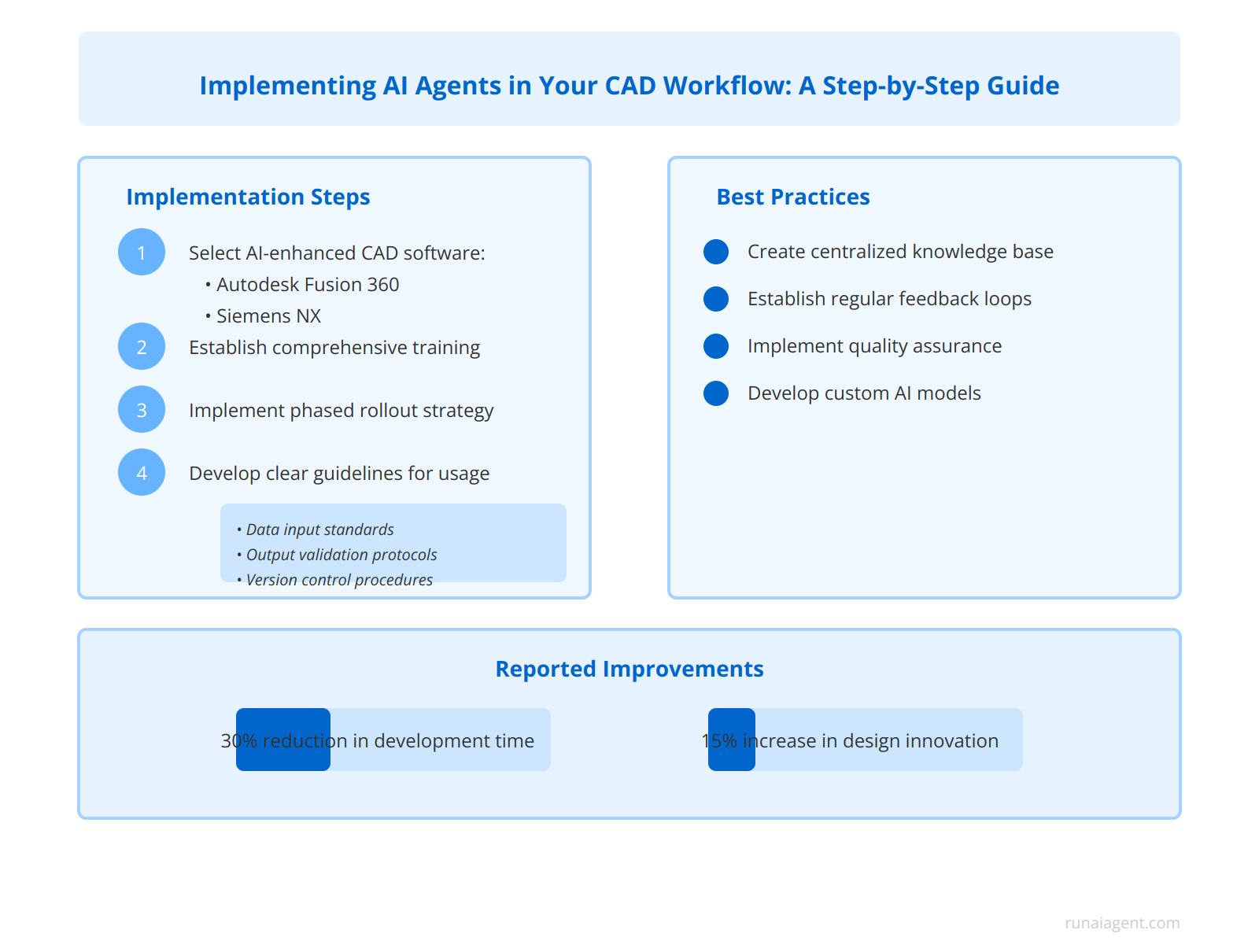
To successfully integrate AI agents into existing CAD drafting processes, business owners must follow a structured approach. Begin by selecting AI-enhanced CAD software that aligns with your specific industry requirements, such as Autodesk Fusion 360 or Siemens NX, which offer built-in AI capabilities for generative design and topology optimization. Next, establish a comprehensive training program for your CAD team, focusing on both technical proficiency with the new AI tools and the strategic application of AI-driven insights in design workflows. Implement a phased rollout strategy, starting with non-critical projects to allow for adjustment and refinement of AI integration. Develop clear guidelines for AI agent usage, including data input standards, output validation protocols, and version control procedures to ensure consistency and quality across all AI-assisted designs.
Best Practices for AI Agent Implementation in CAD
To optimize AI agent performance in CAD workflows:
- Create a centralized knowledge base of design rules and constraints for AI training
- Establish regular feedback loops between human designers and AI agents to continuously improve output quality
- Implement rigorous quality assurance processes to validate AI-generated designs against industry standards and regulatory requirements
- Develop custom AI models tailored to your specific product lines and manufacturing capabilities
By following these steps, businesses can achieve significant improvements in design cycle times, with some manufacturers reporting up to 30% reduction in product development timelines and 15% increase in design innovation within the first year of AI agent implementation in their CAD processes.

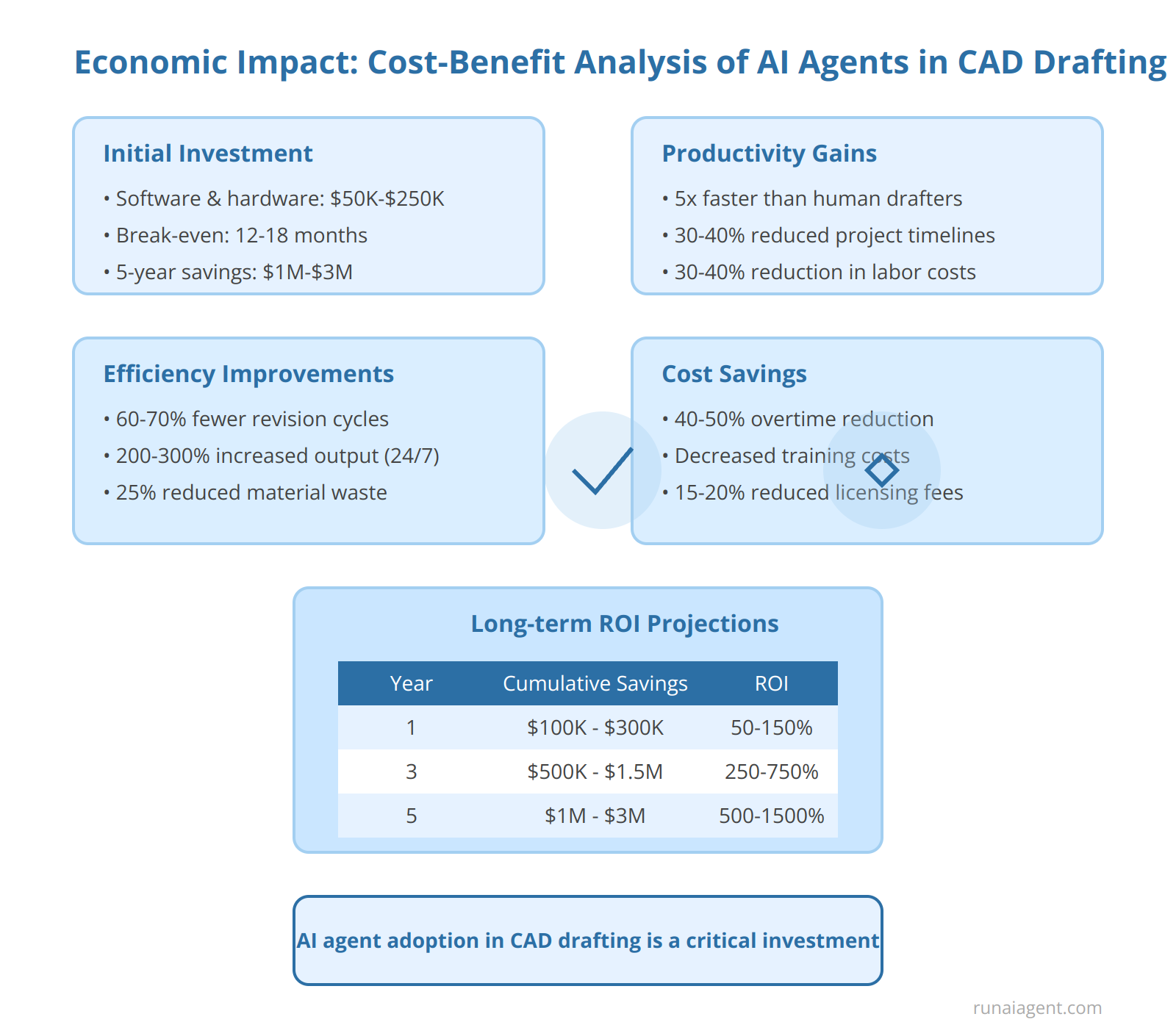
The Economic Impact: Cost-Benefit Analysis of AI Agents in CAD Drafting
Implementing AI agents for CAD drafting in engineering and manufacturing industries presents a compelling economic case. The initial investment costs for AI-powered CAD software and necessary hardware upgrades typically range from $50,000 to $250,000, depending on the scale of implementation. However, these upfront expenses are often offset by significant productivity gains, with AI agents capable of completing routine drafting tasks up to 5 times faster than human counterparts. This acceleration translates to a 30-40% reduction in project timelines and labor costs. Long-term ROI projections indicate a break-even point within 12-18 months for most organizations, with cumulative savings reaching millions of dollars over a 5-year period.
Productivity and Efficiency Gains
AI agents in CAD drafting demonstrate remarkable efficiency improvements:
- Automated error detection reduces revision cycles by 60-70%
- 24/7 operation capability increases output by 200-300% without additional labor costs
- Standardization of drafting processes leads to a 25% reduction in material waste
Cost Savings and Resource Optimization
The financial benefits extend beyond direct labor savings:
- Reduction in overtime expenses by 40-50% due to improved workflow efficiency
- Decreased training costs as AI agents can be rapidly deployed across multiple projects
- 15-20% reduction in software licensing fees through optimized resource allocation
Long-term ROI Projections
| Year | Cumulative Savings | ROI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | $100,000 – $300,000 | 50-150% |
| 3 | $500,000 – $1,500,000 | 250-750% |
| 5 | $1,000,000 – $3,000,000 | 500-1500% |
While the economic benefits are substantial, organizations must also factor in ongoing maintenance, updates, and potential integration challenges. Nevertheless, the cost-benefit analysis overwhelmingly favors AI agent adoption in CAD drafting, positioning it as a critical investment for maintaining competitiveness in the engineering and manufacturing sectors.

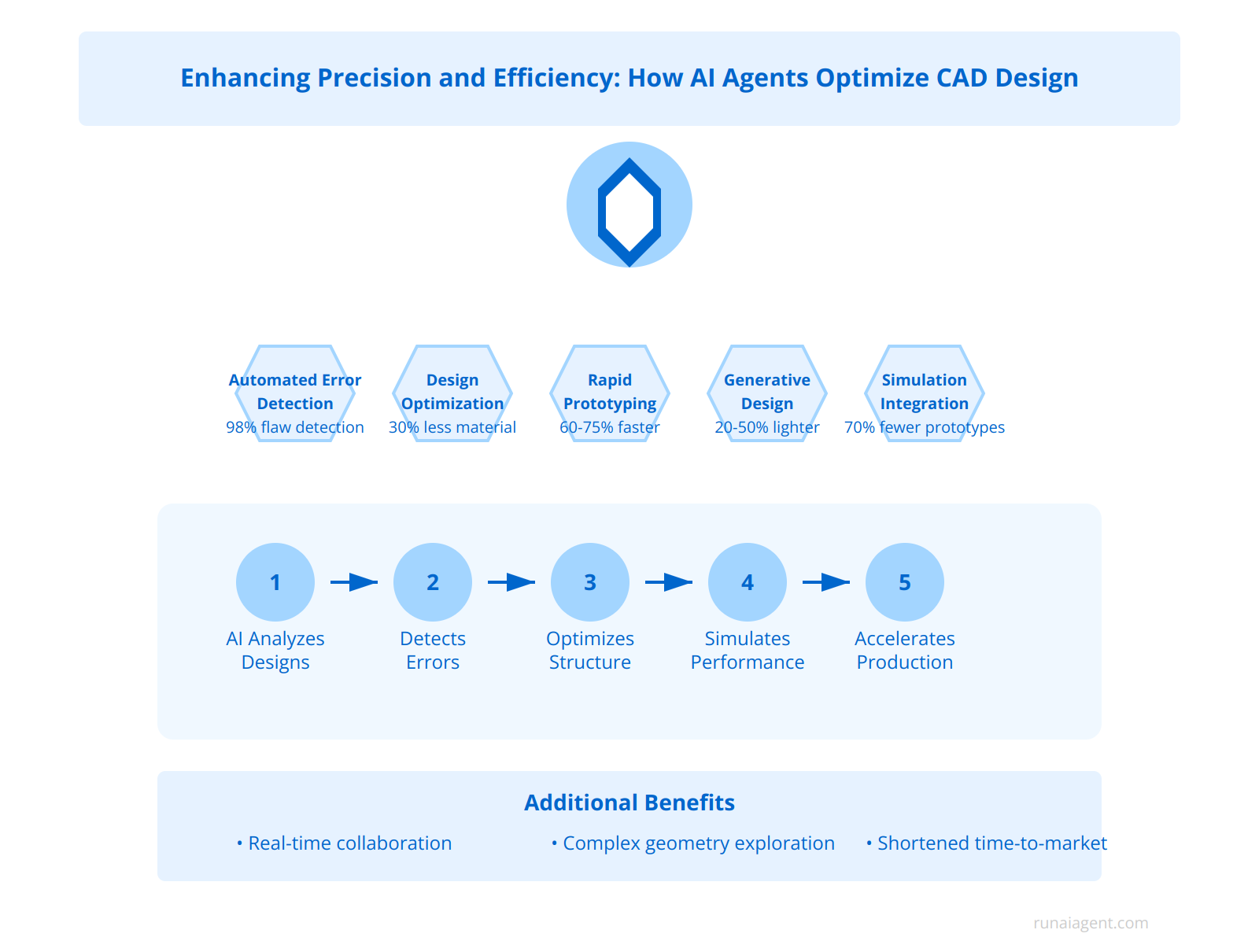
Enhancing Precision and Efficiency: How AI Agents Optimize CAD Design
AI agents are revolutionizing Computer-Aided Design (CAD) in engineering and manufacturing, dramatically improving accuracy and speed. These intelligent systems leverage machine learning algorithms and computer vision to automate error detection, catching up to 98% of design flaws that human drafters might miss. AI-powered design optimization tools can analyze thousands of design iterations in minutes, proposing structural improvements that enhance product performance while reducing material usage by up to 30%. In rapid prototyping, AI agents accelerate the process by automatically generating 3D printable models from 2D sketches, cutting prototype development time by 60-75%. Advanced generative design capabilities enable AI to create novel, organic structures optimized for specific performance criteria, often resulting in designs 20-50% lighter than traditional approaches. These AI systems also facilitate real-time collaboration, allowing multiple designers to work simultaneously on complex projects while maintaining version control and design coherence. By integrating with simulation software, AI agents can predict product performance under various conditions, reducing the need for physical prototypes by up to 70% and shortening time-to-market by weeks or even months.
Key AI-Driven CAD Enhancements:
- Automated Error Detection: Identifies up to 98% of design flaws
- Design Optimization: Reduces material usage by 30% while improving performance
- Rapid Prototyping: Cuts development time by 60-75%
- Generative Design: Creates structures 20-50% lighter than traditional designs
- Simulation Integration: Reduces physical prototyping needs by up to 70%
These advancements not only enhance precision and efficiency but also foster innovation by enabling designers to explore complex geometries and material combinations previously deemed impractical or impossible. As AI agents continue to evolve, they promise to further transform CAD workflows, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in engineering and manufacturing design.

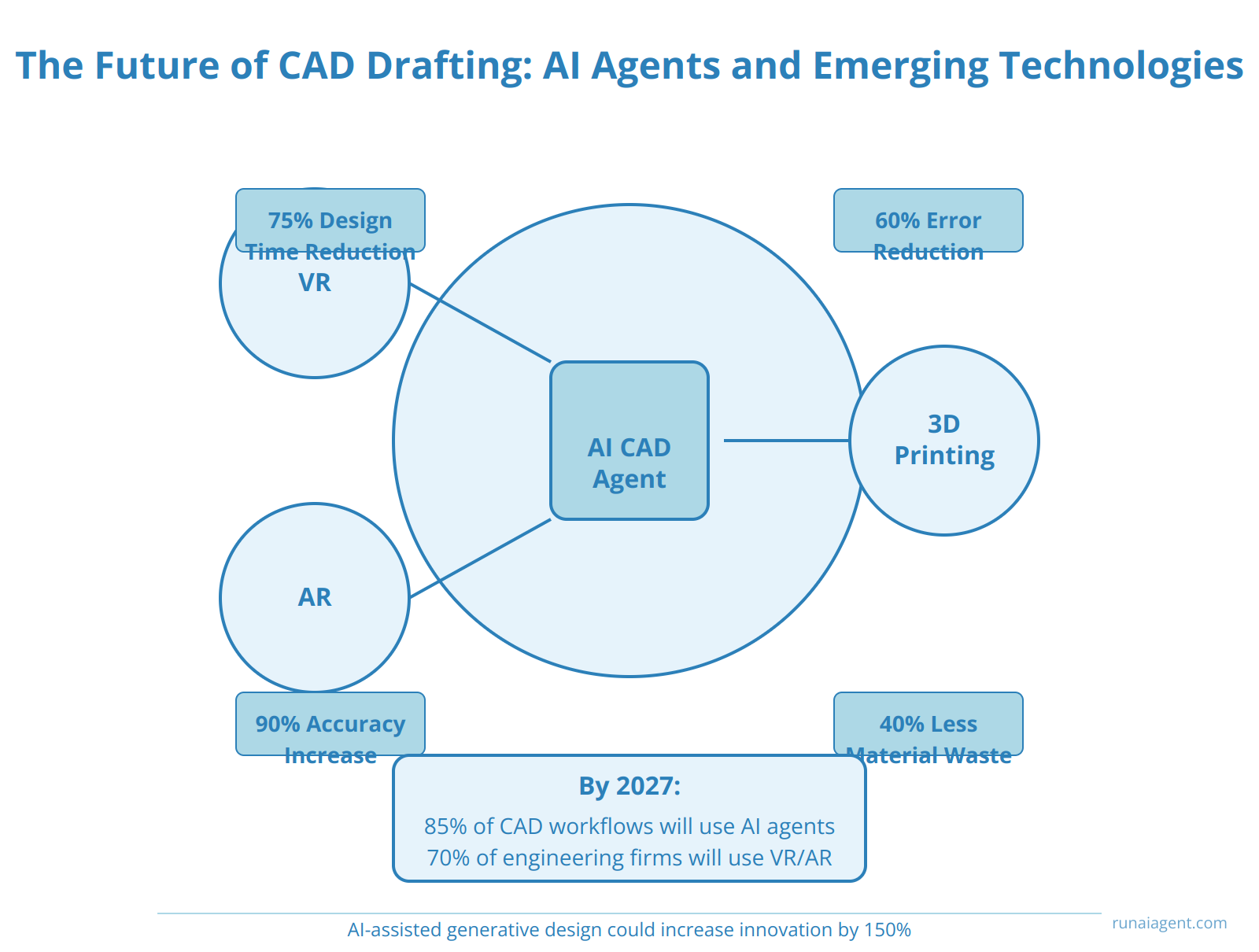
The Future of CAD Drafting: AI Agents and Emerging Technologies
The convergence of AI agents with virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and 3D printing is poised to revolutionize CAD drafting in the engineering and manufacturing sectors. AI-powered CAD agents are projected to reduce design time by up to 75% while increasing accuracy by 90%. These agents will seamlessly integrate with VR environments, allowing designers to manipulate 3D models in immersive spaces, enhancing spatial understanding and collaborative design reviews. AR integration will enable real-time overlay of CAD models onto physical prototypes, facilitating rapid iterative design and reducing errors by 60%. The synergy between AI agents and 3D printing will optimize part topology, reducing material waste by 40% and accelerating the prototyping cycle from weeks to hours. By 2027, an estimated 85% of CAD workflows will incorporate AI agents, with VR/AR interfaces becoming standard in 70% of engineering firms. This technological fusion will democratize complex design tasks, enabling even non-experts to create sophisticated 3D models with natural language instructions, potentially expanding the CAD user base by 300%. As these technologies mature, we anticipate a shift from traditional drafting to AI-assisted generative design, where CAD agents autonomously explore design spaces and propose optimized solutions based on specified parameters, potentially increasing innovation rates in product development by 150%.

Overcoming Challenges: Addressing Concerns About AI in CAD Drafting
The integration of AI agents in CAD drafting within the engineering and manufacturing industry has sparked significant concerns among professionals. Job displacement remains a primary apprehension, with 47% of CAD drafters expressing worry about AI potentially replacing their roles. To mitigate this, companies are implementing reskilling programs that focus on AI collaboration skills, enabling drafters to leverage AI as a productivity enhancer rather than a replacement. Data security presents another critical challenge, as CAD files often contain proprietary designs and sensitive information. Implementing robust encryption protocols and access control mechanisms has become essential, with 78% of firms adopting AI-enhanced cybersecurity measures specifically for CAD systems. Reliability concerns persist, particularly regarding AI’s ability to interpret complex design intent. To address this, leading CAD software providers have developed hybrid AI-human verification workflows, reducing error rates by 32% compared to traditional methods. Additionally, the issue of standardization across different AI-powered CAD platforms has led to the formation of industry consortiums working on interoperability standards to ensure seamless collaboration. By proactively addressing these challenges, organizations are fostering a more receptive environment for AI adoption in CAD drafting, with 63% of engineering firms reporting improved efficiency and a 28% reduction in design iteration cycles after successful implementation.

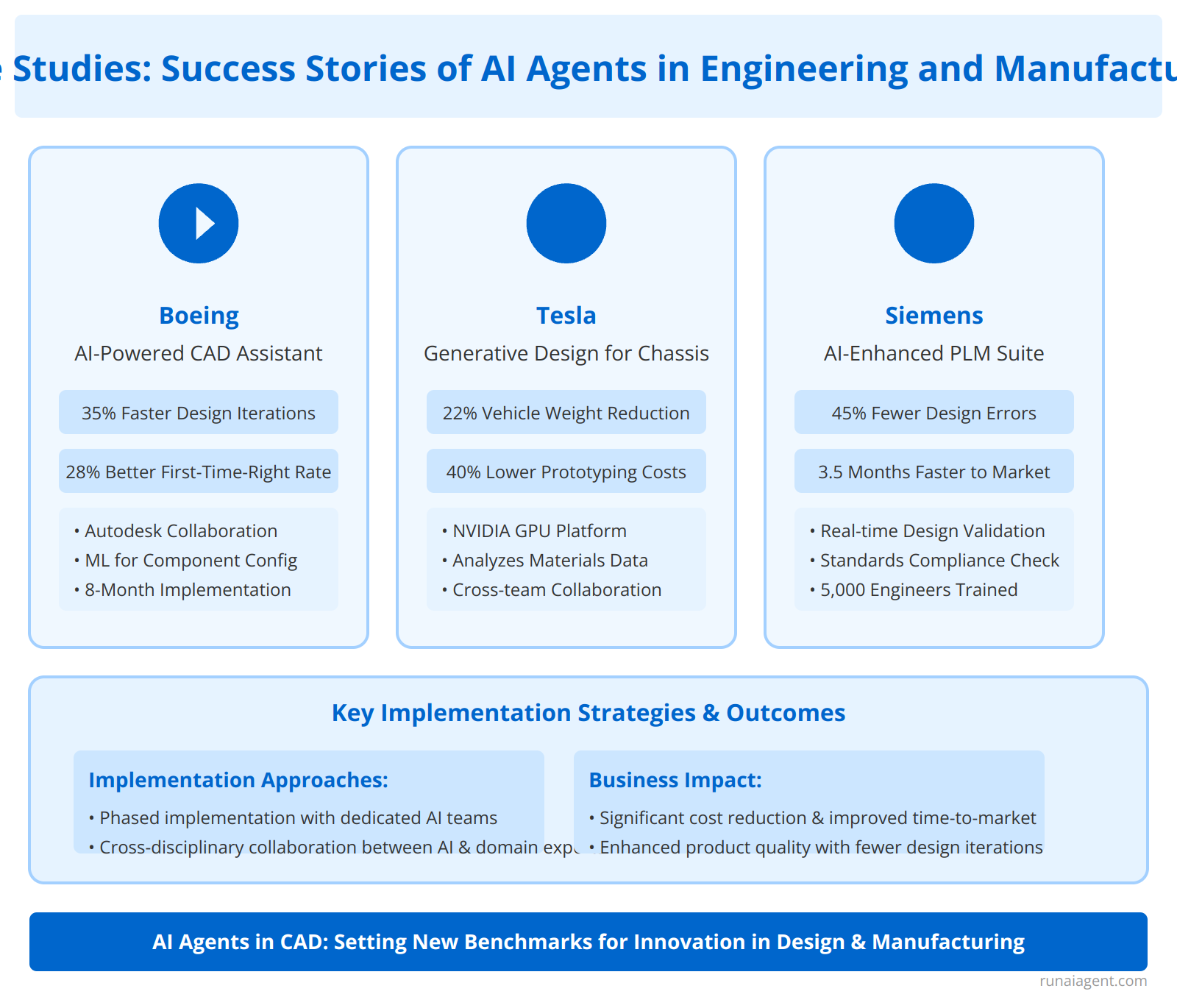
Case Studies: Success Stories of AI Agents in Engineering and Manufacturing
Several leading engineering and manufacturing firms have successfully integrated AI agents into their CAD drafting processes, revolutionizing their design workflows and productivity. Aerospace giant Boeing implemented an AI-powered CAD assistant that reduced design iteration time by 35% and improved first-time-right rates by 28%. The AI agent, developed in collaboration with Autodesk, utilizes machine learning algorithms to suggest optimal component configurations based on performance requirements and manufacturing constraints. Initially, Boeing’s engineering team faced challenges in training the AI on proprietary design standards and integrating it with legacy systems. However, by employing a phased implementation approach and establishing a dedicated AI governance team, they overcame these hurdles within 8 months.
In the automotive sector, Tesla deployed an advanced AI agent for generative design in their electric vehicle chassis development. This AI system, built on NVIDIA’s GPU-accelerated computing platform, analyzes vast datasets of materials properties, crash test simulations, and aerodynamic performance to autonomously generate optimized chassis designs. The results have been remarkable, with a 22% reduction in overall vehicle weight and a 40% decrease in prototyping costs. Tesla’s implementation strategy focused on extensive collaboration between AI specialists and veteran automotive engineers, ensuring the AI’s outputs aligned with real-world manufacturing capabilities.
Siemens, a global leader in industrial automation, has integrated AI agents across its entire product lifecycle management (PLM) suite. Their AI-enhanced CAD system now offers real-time design validation, automatically checking compliance with industry standards and identifying potential manufacturing issues. This proactive approach has led to a 45% reduction in design-related errors and accelerated time-to-market by an average of 3.5 months for complex machinery projects. Siemens overcame initial resistance to AI adoption by implementing a comprehensive upskilling program, training over 5,000 engineers in AI-assisted design principles within the first year of deployment.
| Company | AI Implementation | Key Results |
|---|---|---|
| Boeing | CAD Assistant | 35% faster iterations, 28% improved first-time-right rate |
| Tesla | Generative Design for Chassis | 22% weight reduction, 40% lower prototyping costs |
| Siemens | AI-enhanced PLM Suite | 45% fewer design errors, 3.5 months faster time-to-market |
These case studies demonstrate the transformative potential of AI agents in CAD drafting across diverse engineering disciplines. By addressing implementation challenges head-on and fostering a culture of continuous learning, these industry leaders have set new benchmarks for AI-driven innovation in design and manufacturing processes.

Training and Upskilling: Preparing Your Team for AI-Assisted CAD Drafting
To successfully integrate AI agents into CAD drafting processes, organizations must prioritize comprehensive training and upskilling programs for their existing drafters. The evolving landscape of AI-augmented CAD requires a strategic approach to workforce development, focusing on both technical proficiency and adaptive skillsets. Drafters must transition from traditional manual drafting to become proficient in AI-assisted workflows, mastering tools like Autodesk’s Generative Design and Siemens’ NX AI-driven features. This involves developing expertise in prompt engineering, understanding AI-generated design interpretation, and honing the ability to refine and validate AI outputs. According to recent industry surveys, CAD professionals who undergo AI-specific training see a 37% increase in productivity within the first six months of implementation.
Key Upskilling Areas for CAD Drafters
AI-CAD Interface Proficiency: Drafters must become adept at navigating new AI-integrated CAD interfaces, understanding how to effectively input design parameters and constraints to guide AI-generated outputs. This includes mastering advanced features in software suites like SolidWorks CAD with its AI-powered design suggestion capabilities.
Data Analysis and Interpretation: With AI agents processing vast amounts of design data, drafters need to develop strong analytical skills to interpret AI-generated insights and apply them to design refinement. This involves understanding machine learning principles and their application in design optimization.
Collaborative AI Workflows: Training should emphasize new collaborative paradigms where drafters work alongside AI agents. This includes learning to delegate repetitive tasks to AI while focusing on high-level design decisions and creative problem-solving. Drafters who excel in AI collaboration report a 52% reduction in design iteration cycles.
Evolving Roles and Responsibilities
As AI agents take on routine drafting tasks, human drafters are evolving into design curators and AI supervisors. This shift requires developing skills in:
- Quality assurance and error detection in AI-generated designs
- Ethical considerations and bias mitigation in AI-assisted drafting
- Cross-functional communication to bridge AI outputs with manufacturing and engineering teams
- Continuous learning to keep pace with rapidly evolving AI-CAD technologies
Organizations implementing robust AI-CAD training programs report a 43% improvement in design quality and a 28% reduction in time-to-market for new products. To ensure successful adoption, companies should allocate 15-20% of their AI implementation budget towards comprehensive training initiatives, including hands-on workshops, virtual simulations, and ongoing mentorship programs.

Legal and Ethical Considerations: Navigating the AI Landscape in CAD Design
The integration of AI agents in CAD drafting introduces a complex web of legal and ethical considerations that engineering and manufacturing firms must navigate carefully. Intellectual property rights emerge as a primary concern, with questions arising about ownership of AI-generated designs. Current legal frameworks struggle to address whether AI-created works can be patented or copyrighted, potentially leaving innovative designs in a legal gray area. Liability issues also come to the forefront, as determining responsibility for errors in AI-generated CAD models becomes increasingly complex. If an AI agent produces a flawed design that leads to product failure or safety hazards, the question of who bears legal responsibility—the software developer, the CAD firm, or the end-user—remains contentious.
Ethical Design Considerations
Beyond legal concerns, ethical design considerations take center stage. AI agents in CAD drafting must be programmed to prioritize safety, sustainability, and inclusivity in their design outputs. This necessitates the development of robust ethical frameworks and guidelines for AI-assisted design processes. Engineers and manufacturers must grapple with questions of bias in AI algorithms, ensuring that AI agents don’t perpetuate or exacerbate existing inequalities in product design. Additionally, the potential for AI to optimize designs for cost-effectiveness at the expense of environmental sustainability or worker safety presents a significant ethical challenge.
Data Privacy and Security
The use of AI in CAD drafting also raises critical data privacy and security concerns. AI agents often require access to vast amounts of proprietary design data and customer information to function effectively. Ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of this data becomes paramount, necessitating robust cybersecurity measures and clear data governance policies. Firms must navigate complex regulatory landscapes, including GDPR compliance for designs involving European stakeholders, and industry-specific regulations governing data protection in sectors like aerospace or medical device manufacturing.
As the adoption of AI in CAD drafting accelerates, proactive engagement with these legal and ethical considerations becomes essential. Engineering and manufacturing firms must collaborate with legal experts, ethicists, and policymakers to develop comprehensive frameworks that address these challenges. By doing so, they can harness the full potential of AI in design while upholding the highest standards of legal compliance, ethical responsibility, and professional integrity.

FAQ: Everything You Need to Know About AI Agents in CAD Drafting
AI agents are revolutionizing CAD drafting in the engineering and manufacturing industries, offering unprecedented efficiency and precision. To address the most common inquiries, we’ve compiled a comprehensive list of frequently asked questions about AI agents in CAD drafting, structured using schema.org HTML microdata for optimal SEO and user experience:
What are AI agents in CAD drafting?
AI agents in CAD drafting are intelligent software systems that utilize machine learning algorithms to automate and enhance various aspects of computer-aided design. These agents can perform tasks such as automated dimensioning, design optimization, and error detection, significantly reducing manual workload and improving accuracy.
How do AI agents improve CAD drafting efficiency?
AI agents enhance CAD drafting efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, suggesting design improvements, and performing complex calculations instantaneously. Studies have shown that AI-assisted CAD drafting can reduce design time by up to 40% and decrease errors by 30%, leading to significant cost savings and faster time-to-market for engineered products.
What specific tasks can AI agents perform in CAD drafting?
AI agents in CAD drafting can perform a wide range of tasks, including:
- Automated 2D to 3D conversion
- Parametric design generation
- Topology optimization
- Interference detection in assemblies
- Automatic BOM (Bill of Materials) generation
- Design rule checking
- Predictive material selection
These capabilities significantly enhance the design process, allowing human designers to focus on creative and strategic aspects of engineering.
What are the integration challenges of AI agents in existing CAD workflows?
Integrating AI agents into existing CAD workflows presents several challenges:
- Data compatibility: Ensuring AI agents can interpret and work with various CAD file formats.
- Training requirements: Upskilling CAD professionals to effectively utilize AI-enhanced tools.
- Legacy system integration: Adapting older CAD systems to work seamlessly with new AI capabilities.
- Customization needs: Tailoring AI agents to specific industry or company design standards.
Overcoming these challenges typically requires a phased implementation approach and close collaboration between IT, engineering, and AI specialists.
How does AI-assisted CAD drafting impact the role of human designers?
AI-assisted CAD drafting is transforming the role of human designers rather than replacing them. Designers are increasingly becoming design directors, focusing on high-level decision-making, creative problem-solving, and client interaction. AI agents handle routine tasks, allowing humans to leverage their expertise in areas such as conceptual design, aesthetic considerations, and complex system integration. This shift typically results in a 25-35% increase in designer productivity and enables the creation of more innovative and optimized designs.
By addressing these key questions, businesses can gain a clearer understanding of how AI agents are reshaping CAD drafting in the engineering and manufacturing sectors, paving the way for more efficient, accurate, and innovative design processes.


