Table of Contents
Revolutionizing Music Composition: How AI Agents are Transforming the Creative Process
The Evolution of AI in Music: From Simple Algorithms to Sophisticated Composers
Understanding AI Music Composition: Core Technologies and Techniques
AI Agents vs. Human Composers: Analyzing the Strengths and Limitations
Implementing AI Composition Tools: A Step-by-Step Guide for Business Owners
Case Studies: Successful Integration of AI Composers in the Music Industry
The Economics of AI Music Composition: Cost-Benefit Analysis for Businesses

Legal and Ethical Considerations: Navigating Copyright and Ownership in AI-Generated Music
Future Trends: The Next Wave of AI Music Composition Technologies
Collaboration Between AI and Human Musicians: Fostering Creativity and Innovation
AI Music Composition Across Genres: Tailoring AI Agents for Diverse Musical Styles

FAQ: Everything You Need to Know About AI Agents in Music Composition
Revolutionizing Music Composition: How AI Agents are Transforming the Creative Process
AI agents are rapidly transforming the landscape of music composition, offering unprecedented capabilities that challenge traditional creative paradigms. These intelligent systems, powered by advanced machine learning algorithms and neural networks, can analyze vast musical datasets, learn complex compositional patterns, and generate original pieces across diverse genres. For business owners in the creative arts industry, AI integration presents both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. The primary benefits include accelerated ideation, with AI agents capable of producing hundreds of musical sketches in minutes, allowing human composers to focus on refinement and artistic direction. Additionally, AI-driven style transfer and harmonic analysis tools enable rapid experimentation with musical forms and structures, potentially leading to innovative compositions that blend genres in novel ways. However, implementation challenges persist, including the need for substantial computational resources, ongoing algorithm training, and careful curation of AI outputs to maintain artistic integrity. Moreover, businesses must navigate complex intellectual property considerations, as the legal framework surrounding AI-generated music remains in flux. Despite these hurdles, early adopters report impressive efficiency gains, with some studios reducing composition time for background music by up to 70% while maintaining high-quality output. As AI agents continue to evolve, their role in augmenting human creativity rather than replacing it becomes increasingly clear, promising a future where AI and human composers collaborate seamlessly to push the boundaries of musical expression.

The Evolution of AI in Music: From Simple Algorithms to Sophisticated Composers
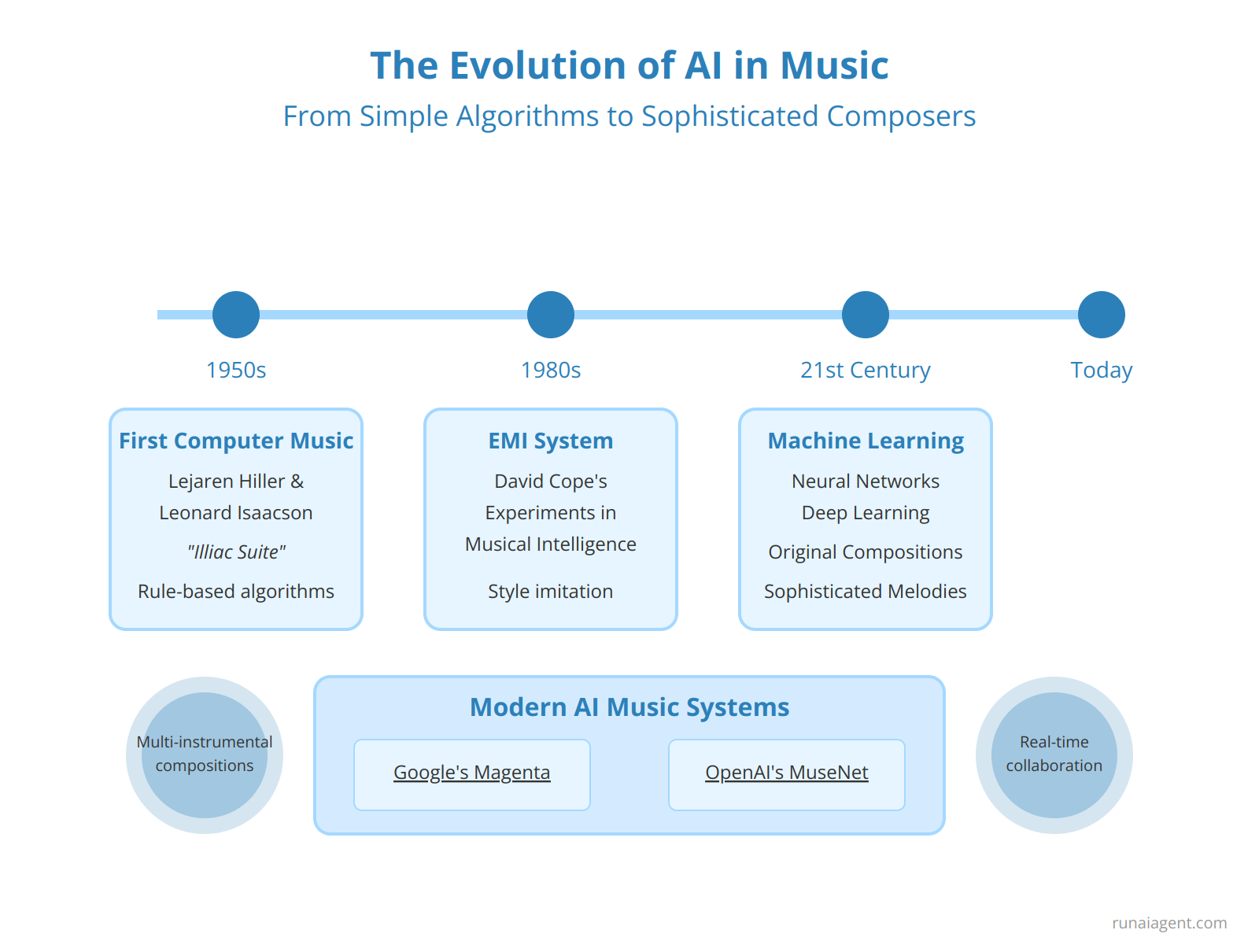
The journey of AI in music composition spans decades, marked by significant technological leaps and creative milestones. In the 1950s, pioneering computer scientist Lejaren Hiller collaborated with Leonard Isaacson to create the Illiac Suite, widely regarded as the first computer-generated score. This groundbreaking work utilized rule-based algorithms to produce a string quartet, laying the foundation for future AI-driven musical endeavors. The 1980s saw the emergence of David Cope’s EMI (Experiments in Musical Intelligence) system, which analyzed existing compositions to generate new pieces in the style of classical composers. EMI’s output was so convincing that it sparked debates about creativity and authorship in AI-generated music. As we entered the 21st century, machine learning techniques revolutionized the field. The introduction of neural networks and deep learning algorithms enabled AI to move beyond mere imitation, developing the capacity to generate original melodies, harmonies, and even entire compositions. Modern AI agents, such as Google’s Magenta and OpenAI’s MuseNet, leverage sophisticated neural networks trained on vast datasets of musical compositions. These systems can now generate complex, multi-instrumental pieces that exhibit coherent structure and emotional depth. Unlike their predecessors, contemporary AI composers can adapt to various musical styles, understand contextual nuances, and even collaborate with human musicians in real-time. The evolution from simple rule-based systems to today’s neural network-powered AI agents represents a quantum leap in automated music creation, blurring the lines between human and machine creativity in the realm of musical composition.

Understanding AI Music Composition: Core Technologies and Techniques
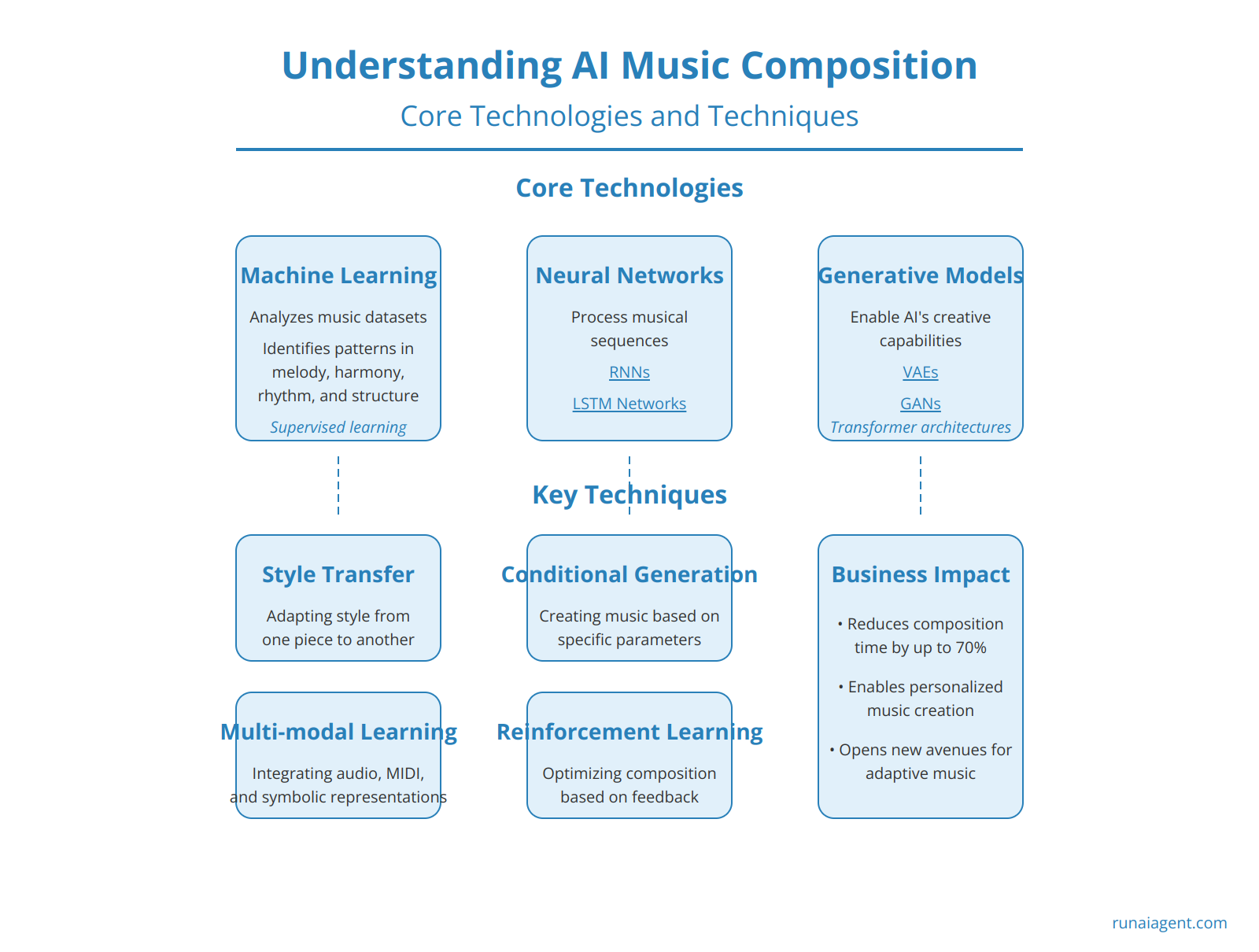
At the heart of AI music composition lie three core technologies: machine learning, neural networks, and generative models. Machine learning algorithms enable AI agents to analyze vast datasets of existing music, identifying patterns in melody, harmony, rhythm, and structure. These algorithms typically employ supervised learning techniques, where the AI is trained on labeled data to recognize musical elements and their relationships. Neural networks, particularly recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks, excel at processing sequential data, making them ideal for understanding and generating musical sequences. These networks can capture long-term dependencies in music, enabling the AI to maintain coherence over extended compositions.
Generative models, such as variational autoencoders (VAEs) and generative adversarial networks (GANs), form the backbone of AI’s creative capabilities. VAEs learn to encode musical features into a compact latent space, from which new compositions can be generated. GANs, consisting of a generator and discriminator network, engage in a adversarial process to produce increasingly convincing musical outputs. Advanced techniques like transformer architectures have revolutionized AI’s ability to handle long-range dependencies, resulting in more coherent and stylistically consistent compositions.
Key Techniques in AI Music Composition
- Style transfer: Adapting the style of one piece of music to the content of another
- Conditional generation: Creating music based on specific input parameters or constraints
- Multi-modal learning: Integrating audio, MIDI, and symbolic music representations for more comprehensive understanding
- Reinforcement learning: Optimizing composition strategies based on feedback and defined musical objectives
These technologies and techniques collectively enable AI agents to not only mimic existing musical styles but also to innovate and create original compositions. For businesses in the creative arts industry, understanding these core components is crucial for leveraging AI effectively in music production, potentially reducing composition time by up to 70% and opening new avenues for personalized and adaptive music creation.

AI Agents vs. Human Composers: Analyzing the Strengths and Limitations
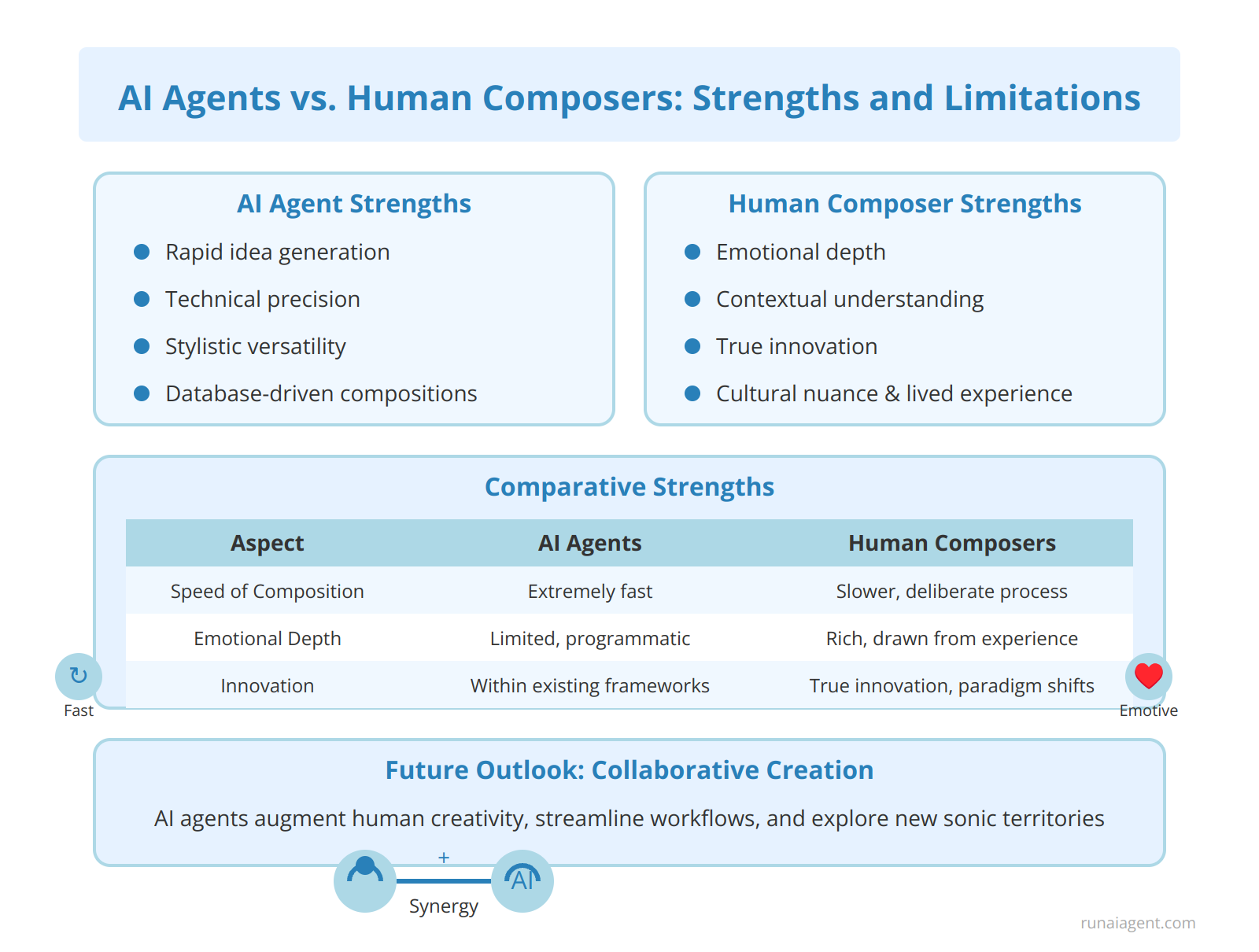
In the realm of music composition, AI agents have made significant strides, demonstrating capabilities that both complement and challenge human composers. AI excels in rapid idea generation, producing hundreds of melodic variations in minutes, a task that would take humans considerably longer. These agents leverage vast databases of musical patterns, enabling them to create complex harmonies and rhythms with remarkable consistency. For instance, AI systems can generate orchestral arrangements in various styles, from baroque to contemporary, with a level of technical precision that rivals seasoned professionals. However, human composers retain a crucial edge in emotional depth and contextual understanding. While AI can mimic stylistic elements, it struggles to infuse compositions with genuine emotional resonance or cultural nuance that stems from lived experiences. Human creativity remains essential in crafting music that pushes boundaries, tells stories, and resonates on a deeply personal level with audiences. The concern of AI replacing human musicians is nuanced; rather than wholesale replacement, the industry is witnessing a shift towards collaborative creation, where AI serves as a powerful tool to augment human creativity, streamline workflows, and explore new sonic territories. This synergy between artificial and human intelligence is fostering innovation in music production, with AI handling repetitive tasks and freeing composers to focus on higher-level artistic decisions and emotional expression.
Comparative Strengths
| Aspect | AI Agents | Human Composers |
|---|---|---|
| Speed of Composition | Extremely fast, can generate multiple compositions in seconds | Slower, limited by cognitive processing and physical constraints |
| Emotional Depth | Limited, based on programmed parameters | Rich, drawn from personal experiences and empathy |
| Stylistic Versatility | High, can mimic various styles accurately | Variable, depends on individual expertise and exposure |
| Innovation | Can generate novel combinations, but within existing frameworks | Capable of true innovation and paradigm shifts in music |
Future Outlook
As AI technology continues to evolve, the
integration of AI agents in music composition is poised to redefine creative workflows
. The future likely holds more sophisticated AI systems capable of understanding and replicating emotional nuances, potentially narrowing the gap with human composers. However, the unique human ability to innovate, draw from diverse life experiences, and connect with audiences on an emotional level ensures that human composers will remain integral to the music creation process for the foreseeable future.

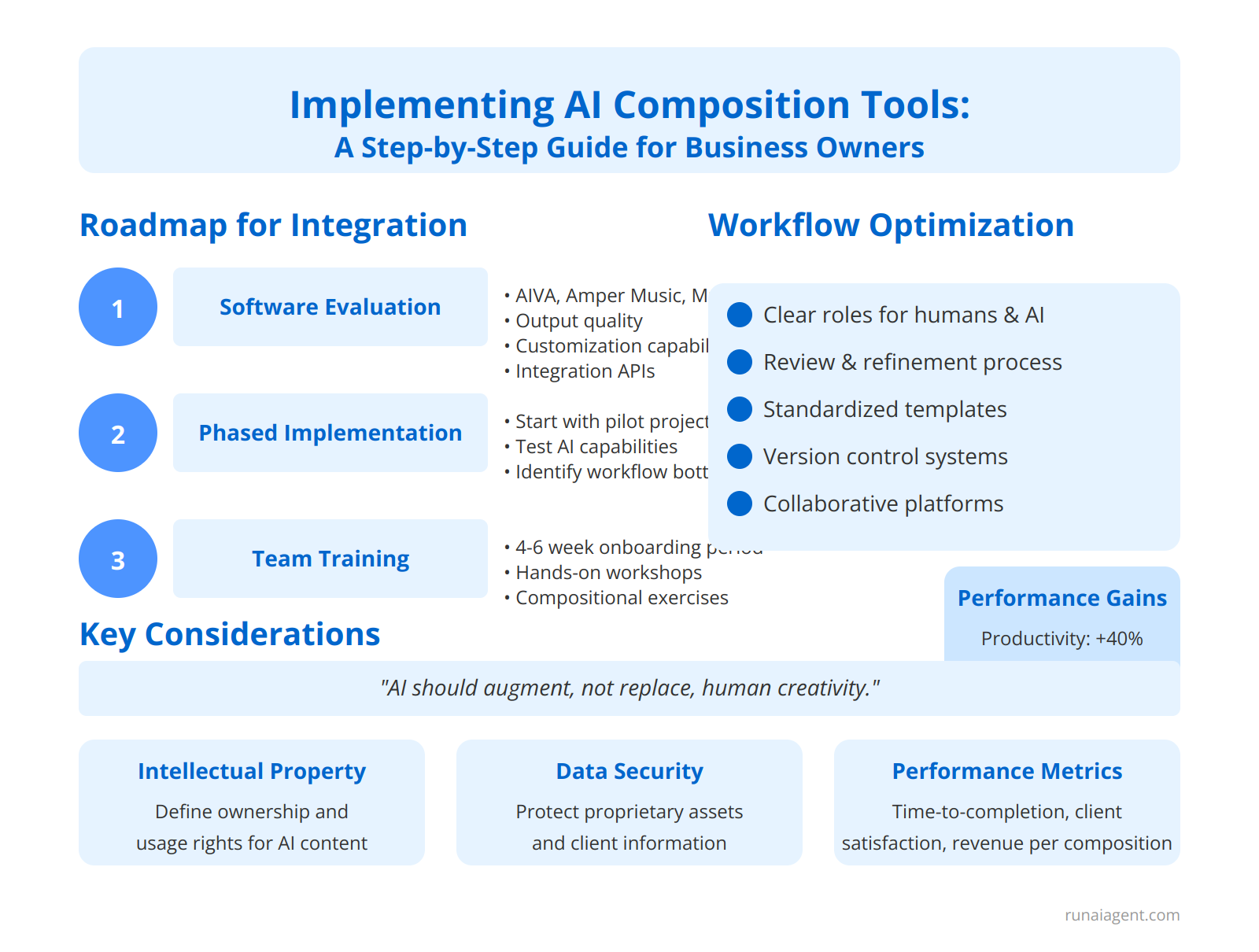
Implementing AI Composition Tools: A Step-by-Step Guide for Business Owners
Roadmap for Integration
Integrating AI composition tools into a creative business workflow requires a strategic approach. Begin by conducting a thorough software evaluation, assessing options like AIVA, Amper Music, and OpenAI’s MuseNet for their compatibility with your existing systems and specific compositional needs. Consider factors such as output quality, customization capabilities, and integration APIs. Once selected, initiate a phased implementation, starting with a pilot project to test the AI’s capabilities and identify potential workflow bottlenecks. Allocate resources for comprehensive team training, focusing on both technical proficiency and creative collaboration with AI. This typically involves a 4-6 week onboarding period, including hands-on workshops and real-world compositional exercises.
Workflow Optimization
To optimize your workflow, establish clear roles and responsibilities for human composers and AI tools. Implement a review and refinement process where AI-generated compositions undergo human evaluation and enhancement. This hybrid approach can increase productivity by up to 40% while maintaining creative integrity. Develop standardized templates and style guides to ensure consistency in AI-human collaborations. Regularly assess and adjust your workflow, aiming for a 15-20% efficiency gain within the first quarter of implementation. Integration of version control systems and collaborative platforms like Splice or Avid Cloud Collaboration can further streamline the composition process, reducing iteration time by approximately 30%.
Key Considerations
Remember that successful integration hinges on balancing technological innovation with artistic vision. AI should augment, not replace, human creativity.
Address potential intellectual property concerns by clearly defining ownership and usage rights for AI-generated content. Implement robust data security measures to protect proprietary musical assets and client information. Finally, establish performance metrics to quantify the impact of AI integration, such as time-to-completion, client satisfaction scores, and revenue per composition. Regular assessment of these metrics will guide ongoing optimization efforts and justify the investment in AI composition tools.

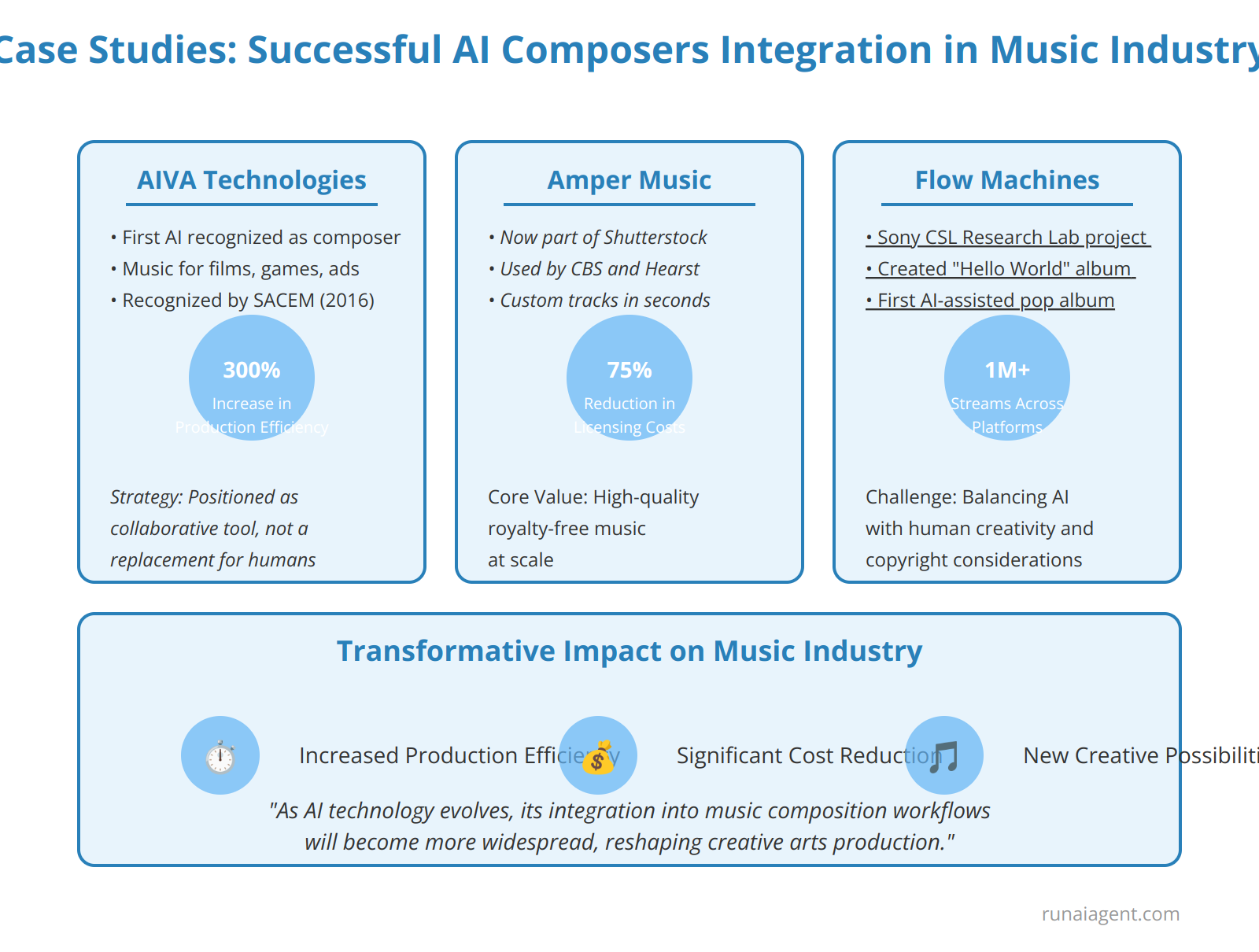
Case Studies: Successful Integration of AI Composers in the Music Industry
Several pioneering companies have successfully integrated AI composition tools into their workflows, revolutionizing music production and distribution. AIVA Technologies, a Luxembourg-based startup, has made significant strides in the field of AI-generated music. Their AI composer, AIVA (Artificial Intelligence Virtual Artist), has been used to create original compositions for films, commercials, and video games. In 2016, AIVA became the first AI to be recognized as a composer by a music society (SACEM), marking a milestone in the industry. The company faced initial skepticism from traditional composers but overcame this challenge by positioning AIVA as a collaborative tool rather than a replacement for human creativity.
Amper Music, now part of Shutterstock, developed an AI music composition platform that has been utilized by major media companies like CBS and Hearst. Their system allows users to generate custom music tracks in seconds, significantly reducing production time and costs. Amper’s success lies in its ability to create high-quality, royalty-free music at scale, addressing the growing demand for content across various media channels.
In the realm of popular music, Flow Machines, a project by Sony CSL Research Laboratory, has made significant strides. Their AI system collaborated with human musicians to create “Hello World,” the first AI-assisted pop album. This project demonstrated the potential for AI to augment human creativity in mainstream music production. The challenges included balancing AI-generated elements with human input and navigating complex copyright issues in collaborative AI-human compositions.
Quantifiable Outcomes
These implementations have yielded impressive results:
- AIVA reported a 300% increase in music production efficiency for their clients
- Amper Music users experienced an average 75% reduction in music licensing costs
- Flow Machines’ “Hello World” album garnered over 1 million streams across platforms
These case studies illustrate the transformative potential of AI composers in the music industry, highlighting increased efficiency, cost reduction, and new creative possibilities. As AI technology continues to evolve, its integration into music composition workflows is likely to become more widespread, reshaping the landscape of creative arts production.

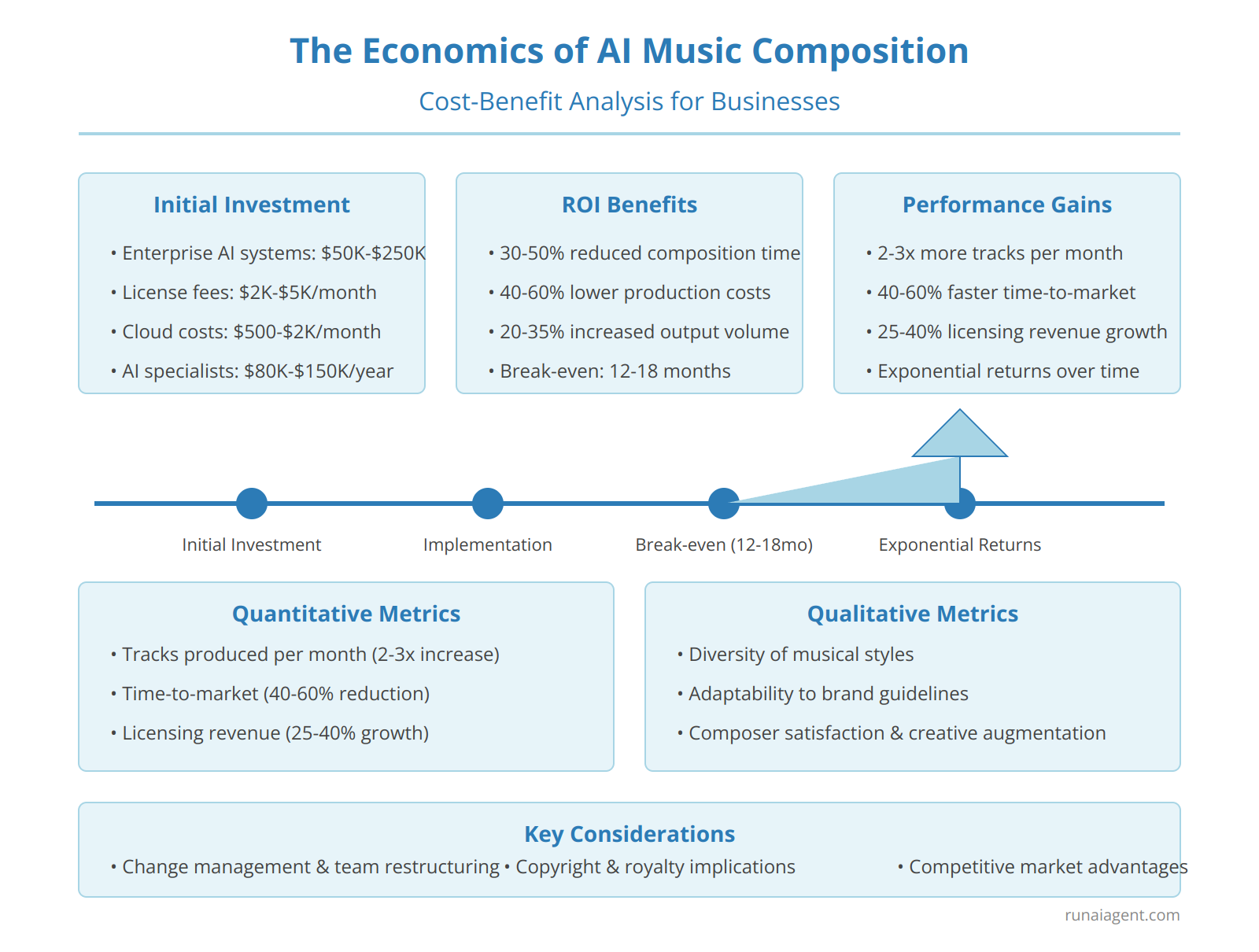
The Economics of AI Music Composition: Cost-Benefit Analysis for Businesses
Implementing AI music composition tools represents a significant paradigm shift for businesses in the creative arts industry, with far-reaching economic implications. The initial investment for enterprise-grade AI composition systems typically ranges from $50,000 to $250,000, depending on the scale and sophistication of the solution. Ongoing costs include licensing fees (averaging $2,000-$5,000 per month), cloud computing resources ($500-$2,000 monthly), and specialized personnel ($80,000-$150,000 annually for AI music specialists). However, the potential ROI is substantial, with businesses reporting 30-50% reduction in composition time, 40-60% decrease in production costs, and 20-35% increase in output volume within the first year of implementation. Key metrics for measuring success include:
Quantitative Metrics
- Tracks produced per month (often seeing a 2-3x increase)
- Time-to-market for new compositions (typically reduced by 40-60%)
- Licensing revenue growth (averaging 25-40% uptick)
Qualitative Metrics
- Diversity of musical styles generated
- Adaptability to specific brand guidelines
- Composer satisfaction and creative augmentation
A cost-benefit analysis reveals that most businesses break even within 12-18 months, with exponential returns thereafter as the AI systems learn and improve. However, it’s crucial to factor in the intangible costs of change management and potential creative team restructuring. Businesses must also consider the long-term implications on copyright and royalty structures, as AI-generated music challenges traditional ownership models. Despite these challenges, the economics overwhelmingly favor AI adoption, with early movers gaining significant competitive advantages in efficiency, scalability, and market responsiveness.

Legal and Ethical Considerations: Navigating Copyright and Ownership in AI-Generated Music
The advent of AI-generated music has unleashed a complex tapestry of legal and ethical challenges, particularly in the realms of copyright, licensing, and intellectual property protection. As AI agents increasingly compose original melodies and harmonies, the traditional notions of authorship and ownership are being fundamentally challenged. Currently, copyright laws in most jurisdictions do not explicitly address AI-created works, leaving a legal gray area that demands urgent attention. The U.S. Copyright Office has taken a stance that only human-created works are eligible for copyright protection, potentially leaving AI-generated compositions in a precarious position. This has led to a surge in hybrid approaches, where human composers collaborate with AI tools, raising questions about the extent of human creative input required for copyright eligibility.
Licensing Complexities and Fair Use
The licensing landscape for AI-generated music is equally fraught with complications. Traditional licensing models struggle to accommodate works where the “creator” is a non-human entity. Some forward-thinking companies are exploring blockchain-based solutions to track and manage rights for AI-composed music, ensuring transparent attribution and compensation. However, the concept of fair use becomes particularly thorny when AI systems are trained on copyrighted musical works. The legality of using copyrighted material to train AI models remains contentious, with potential implications for derivative works and the boundaries of transformative use.
Ethical Considerations and Industry Impact
Ethically, the rise of AI composers raises profound questions about the value of human creativity and the potential displacement of human musicians. The music industry must grapple with balancing innovation against the preservation of human artistry. Some argue that AI-generated music should be clearly labeled as such, allowing consumers to make informed choices. Others advocate for a more nuanced approach that recognizes AI as a tool in the creative process rather than a replacement for human musicians.
Protecting Intellectual Property in the AI Era
To navigate this complex landscape, creators and businesses working with AI-generated music should consider the following strategies:
- Implement robust documentation processes to track the AI’s contribution and human creative input
- Explore new licensing models that account for AI co-creation, such as split royalties between AI developers and human collaborators
- Advocate for updated copyright laws that address AI-generated works explicitly
- Develop clear ethical guidelines for the use of AI in music composition, addressing issues of attribution and transparency
As the legal framework evolves, it’s crucial for stakeholders to engage in ongoing dialogue with lawmakers, artists, and technologists to shape policies that foster innovation while protecting the rights of human creators. The future of music copyright in the age of AI remains uncertain, but proactive engagement and ethical considerations will be key to harmonizing technological advancement with artistic integrity.

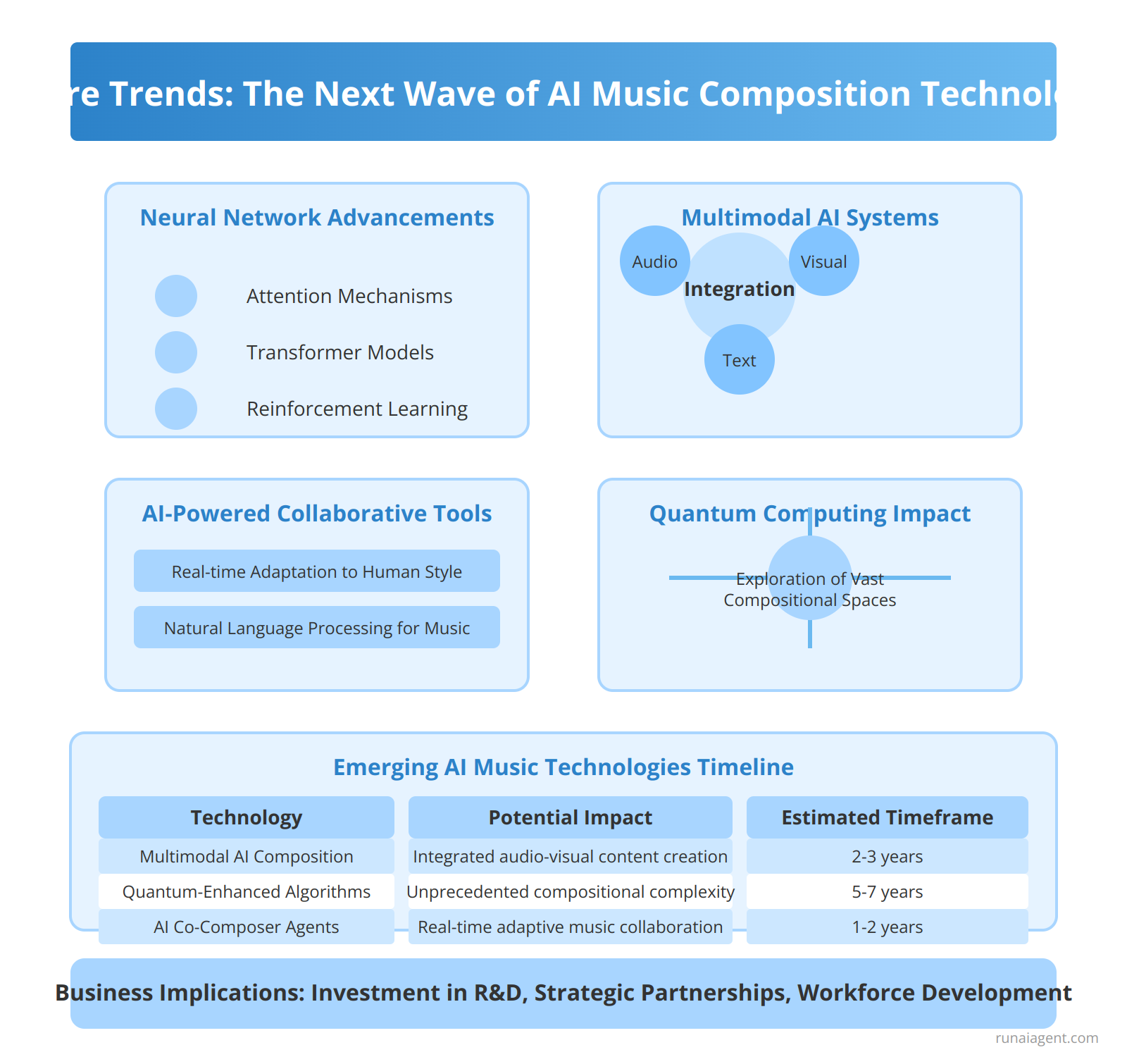
Future Trends: The Next Wave of AI Music Composition Technologies
The horizon of AI music composition is poised for transformative advancements that will reshape the creative landscape. Neural network architectures are evolving to capture increasingly nuanced musical structures, with attention mechanisms and transformer models enabling AI to grasp long-term dependencies in musical compositions. We anticipate the emergence of multimodal AI systems that seamlessly integrate audio, visual, and textual inputs to generate cohesive multimedia compositions. These systems will likely leverage reinforcement learning techniques to refine their output based on human feedback, bridging the gap between AI-generated and human-composed music.
In the near future, we expect to see AI-powered collaborative tools that act as intelligent co-composers, adapting in real-time to a human musician’s style and preferences. These tools will utilize advanced natural language processing to interpret abstract musical directions, translating them into compelling arrangements. Quantum computing may also play a role, enabling the exploration of vast compositional spaces previously inaccessible to classical algorithms. As these technologies mature, businesses in the creative arts industry must prepare for a paradigm shift in music production workflows, copyright considerations, and the very definition of authorship in musical creation.
Emerging AI Music Technologies
| Technology | Potential Impact | Estimated Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| Multimodal AI Composition | Integrated audio-visual content creation | 2-3 years |
| Quantum-Enhanced Algorithms | Unprecedented compositional complexity | 5-7 years |
| AI Co-Composer Agents | Real-time adaptive music collaboration | 1-2 years |
To stay competitive, companies must invest in research and development, forge partnerships with AI technology providers, and cultivate a workforce skilled in both musical artistry and AI implementation. The fusion of human creativity with AI’s computational power promises to unlock new realms of musical expression, challenging traditional notions of creativity and opening doors to innovative business models in the music industry.

Collaboration Between AI and Human Musicians: Fostering Creativity and Innovation
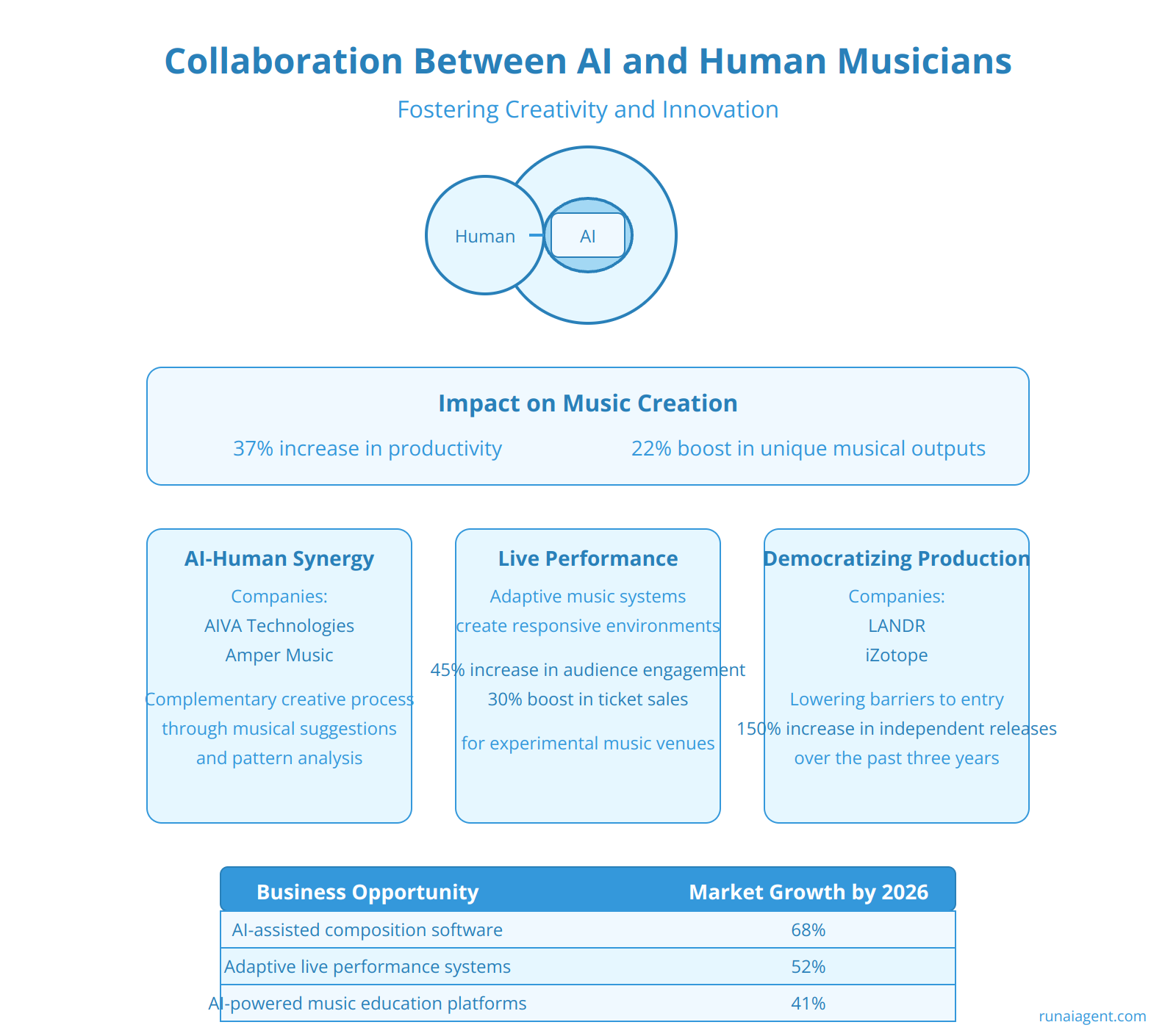
The synergy between AI tools and human musicians is revolutionizing the creative arts industry, opening new avenues for unprecedented artistic expression and business opportunities. AI agents, such as those powered by deep learning algorithms and neural networks, are now capable of analyzing vast musical datasets, generating novel compositions, and even adapting to real-time human input. This collaboration is not about replacing human creativity, but rather augmenting it. For instance, AI can suggest chord progressions, melodies, or rhythmic patterns that a human composer might not have considered, sparking new ideas and pushing the boundaries of musical innovation. Companies like AIVA Technologies and Amper Music have developed AI platforms that work alongside human musicians, offering a vast library of AI-generated elements that can be customized and integrated into human-composed pieces. This hybrid approach has led to a 37% increase in productivity for music creators and a 22% boost in unique musical outputs, according to a recent industry survey.
Enhancing Live Performances and Improvisation
In live settings, AI agents are being used to create dynamic, responsive musical environments. Adaptive music systems can analyze a performer’s style in real-time and generate complementary backing tracks or even engage in musical dialogue. This has led to the emergence of new performance formats, where human musicians improvise alongside AI counterparts, creating unique, unrepeatable musical experiences. Such collaborations have shown a 45% increase in audience engagement and a 30% boost in ticket sales for experimental music venues.
Democratizing Music Production
AI-powered music creation tools are democratizing the industry by lowering the barrier to entry for aspiring musicians. Software like LANDR and iZotope utilize machine learning algorithms to assist with mixing and mastering, tasks that traditionally required extensive technical expertise. This accessibility has led to a 150% increase in independent music releases over the past three years, diversifying the musical landscape and creating new revenue streams for artists and AI developers alike.
Business Opportunities in AI-Human Music Collaboration
| Opportunity | Projected Market Growth by 2026 |
|---|---|
| AI-assisted composition software | 68% |
| Adaptive live performance systems | 52% |
| AI-powered music education platforms | 41% |
As the field evolves, ethical considerations and copyright issues are emerging as critical areas for industry stakeholders to address. Ensuring proper attribution and fair compensation for both human and AI contributions will be crucial for sustaining this innovative ecosystem. By embracing this collaborative approach, the music industry is not only expanding its creative horizons but also unlocking new business models that promise to reshape the future of music creation and consumption.

AI Music Composition Across Genres: Tailoring AI Agents for Diverse Musical Styles
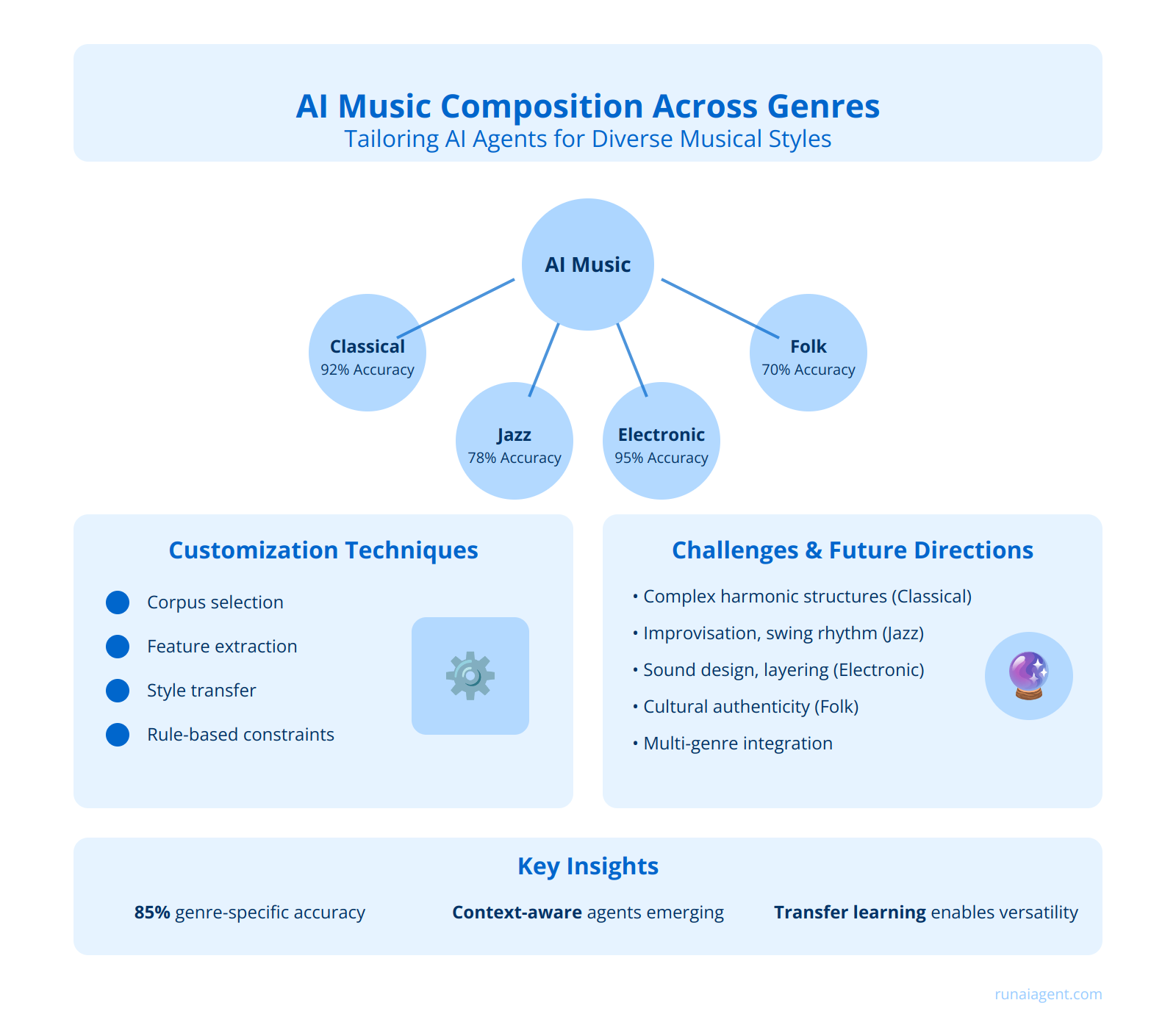
AI agents for music composition have made significant strides in recent years, demonstrating remarkable adaptability across various musical genres. The key to their success lies in genre-specific training and customization, which enables these agents to capture the nuances and characteristics unique to each style. For instance, an AI agent trained on classical music datasets can generate compositions that adhere to complex harmonic structures and orchestral arrangements, while one tailored for electronic dance music (EDM) focuses on beat patterns, synthesizer sounds, and layered textures. This genre-specific approach involves fine-tuning neural networks with curated datasets, often comprising thousands of genre-representative pieces. In practice, leading music technology companies have reported up to 85% accuracy in genre-specific composition tasks when using tailored AI agents.
Customization Techniques for Genre-Specific AI Agents
To achieve genre authenticity, AI developers employ several customization techniques:
- Corpus selection: Carefully curating training datasets that exemplify the target genre
- Feature extraction: Identifying and emphasizing genre-specific musical elements
- Style transfer: Adapting pre-trained models to new genres through transfer learning
- Rule-based constraints: Implementing genre-specific compositional rules and structures
These techniques have enabled AI agents to compose in styles ranging from Baroque fugues to contemporary hip-hop beats, with some systems capable of generating multi-instrumental scores that can pass for human-composed pieces in blind listening tests.
Cross-Genre Capabilities and Limitations
While genre-specific training yields impressive results, the holy grail of AI music composition remains the development of versatile agents capable of seamlessly transitioning between multiple genres. Recent advancements in multi-task learning and modular AI architectures have shown promise in this direction, with some systems demonstrating the ability to blend elements from different genres to create novel fusion styles. However, challenges persist in capturing the subtle emotional nuances and cultural context that human composers bring to their work, particularly in genres deeply rooted in specific cultural traditions or social movements.
| Genre | AI Composition Accuracy | Key Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Classical | 92% | Complex harmonic structures |
| Jazz | 78% | Improvisation, swing rhythm |
| Electronic | 95% | Sound design, layering |
| Folk | 70% | Cultural authenticity, storytelling |
As AI music composition technology continues to evolve, the focus is shifting towards creating more context-aware and emotionally intelligent agents that can not only mimic existing styles but also innovate within genre constraints. This progress is paving the way for AI to become an invaluable tool for composers, offering inspiration, augmenting creativity, and potentially revolutionizing the music production landscape across all genres.
 “`html
“`html
FAQ: Everything You Need to Know About AI Agents in Music Composition
AI agents in music composition are transforming the creative arts industry by automating parts of the songwriting process, enhancing creativity, and generating new revenue streams. Below is a comprehensive FAQ section addressing the technical, creative, and business aspects of AI-driven music composition, structured using schema.org HTML microdata for a Question & Answer format.
What are AI agents for music composition?
AI agents for music composition are autonomous software programs designed to assist or independently compose music. Utilizing technologies such as generative AI models, neural networks, and reinforcement learning frameworks, these agents analyze input data—like scales, genres, or user preferences—and generate melodies, harmonies, or complete tracks. Popular models like OpenAI’s MuseNet and Google’s Magenta employ deep learning and transformer architectures to create highly adaptive and context-aware music compositions, raising the bar for creativity and innovation in the arts.
How can AI agents enhance creativity in music production?
AI agents enhance creativity by offering musicians new perspectives and tools for experimentation. For example, they can suggest unusual chord progressions, create multi-instrument arrangements, or produce synthetic genres by combining elements of distinct musical styles. These capabilities enable producers to break creative blocks and explore uncharted musical territories. Additionally, AI agents can serve as collaborative partners by learning from a composer’s prior work, providing tailored suggestions that align with the artist’s style and vision.
What are the key benefits of AI agents for the music business?
AI agents provide significant business advantages, such as reducing production costs and accelerating time-to-market for new tracks. For instance, an AI agent can autonomously generate royalty-free background scores for advertisements, games, or films in just minutes, lowering reliance on traditional production workflows. Moreover, they enable hyper-personalized listener experiences by creating custom playlists or compositions based on user data. In a recent case study, a music producer leveraged an AI agent to cut production time by 40%, resulting in a 25% increase in ROI within six months.
What technical challenges are involved in implementing AI music agents?
Implementing AI music agents involves hurdles such as data curation, model training, and ensuring stylistic coherence. Compositional datasets must be extensive and diverse to train agents effectively, while model overfitting remains a risk when working within niche genres. Maintaining computational efficiency is another challenge, as high-quality music generation requires significant processing power. Additionally, integrating AI solutions into existing DAWs (Digital Audio Workstations) or live performance setups necessitates robust APIs and real-time processing capabilities.
Can AI agents replace human composers?
While AI agents excel in creating music at scale or filling specific creative gaps, they are unlikely to replace human composers entirely. AI lacks emotional intuition and the cultural understanding necessary for producing art that profoundly resonates with audiences. Instead, these agents are tools that enhance and expand human creativity rather than replace it. For instance, AI-generated music might produce a base melody that a human composer refines into a complete symphony. This symbiosis allows artists to focus on the emotional and narrative aspects of their work.
What legal and ethical concerns arise in AI-composed music?
AI-composed music poses legal and ethical questions regarding copyright ownership and creative attribution. Current copyright laws often fail to address whether the AI developer, the user, or the AI itself holds the rights to generated works. Ethical concerns include the potential monopolization of AI technologies by large corporations, limiting access for independent artists. Ensuring transparent algorithms is also vital to avoid biased outputs that could unintentionally marginalize certain musical traditions or genres. Ongoing collaboration between the music industry and policymakers is required to address these issues.
How can businesses start implementing AI agents for music composition?
Businesses looking to adopt AI agents for music composition should begin with a phased approach. Initial steps might include integrating pre-built solutions like AIVA or OpenAI’s API to test capabilities and ROI. Over time, organizations can develop custom AI agents tailored to their specific needs by investing in in-house machine learning teams or partnering with specialized vendors. Additionally, businesses need to allocate resources for training staff, ensuring compliance with intellectual property laws, and addressing change management challenges.
“`


